Multimedia Gallery
Common cold
Most people have a general idea that when they start sneezing, their nose is runny, and their throat is scratchy, they're getting a cold. But what do you do about it?
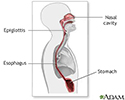
The common cold is something very common that people usually get on average three or more times during a year. And it is a virus that's primarily in the nose.
The three main symptoms of a cold are sneezing, nasal stuffiness, and runny nose. You may have other symptoms, like having a fever of 100? or 101?, or you may have some tickling or scratchiness in the back of your throat. In fact, that may be the very first symptom, a little scratch in the back of your throat. Then after a couple days the nasal discharge tends to turn a little bit darker, maybe a little greener. Then after about a week, you're all the way better.
So, what's the best way to treat a cold?
The first thing you need is plenty of rest and fluids. Water, juice, and clear broth can help replace fluids you may lose during a fever. Chicken soup is another great choice, in fact, it can help relieve congestion. In short, chicken soup really is good food.
Over-the-counter oral cold and cough medicines may help ease adult symptoms, but they don't treat the virus that caused your cold. In fact, so far there is no cure for the common cold. ALSO, don't give a child under 6 any cold medicines, they won't help your child, and they may have serious side effects. And antibiotics? They won't help a cold, and, if you take them too often, antibiotics can break down your body's ability to benefit from them in the future when you may really need them, such as when you get the flu.
In general, remember that getting plenty of rest and fluids is the best way to help you deal with your cold symptoms. Eventually, your cold symptoms usually go away, probably in about a week. If you still feel sick after a week, see your doctor to rule out a sinus infection, allergies, or any other medical problem.
Common cold
Review Date: 10/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Animations
- Abdominal pain
- ACL injury
- Acne
- Adenoid removal
- Adolescent depression
- After your child's ear tube...
- After your child's inguinal...
- After your child's tonsil o...
- After your child's umbilica...
- Allergic rhinitis
- Allergies
- Allergies
- Allergy testing
- Allergy to mold - animal da...
- Anemia
- Ankle ligament injury
- Anterior shoulder stretch
- Anti-reflux surgery
- Appendectomy
- Appendicitis
- Arm reach
- Arrhythmias
- Asperger syndrome
- Asthma
- Asthma - children
- Atopic dermatitis
- Attention deficit hyperacti...
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Before a child's tonsil or ...
- Bipolar disorder
- Bone fracture repair
- Bronchitis
- Bronchoscopy
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cerebral palsy
- Childhood obesity
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Cluster headache
- Cold treatments for kids
- Colorectal polyps
- Common cold
- Concussion
- Concussion
- Crohn disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Cystic fibrosis - nutrition...
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Dialysis
- Diarrhea
- Ear infection - acute
- Ear infection - chronic
- Ear tube insertion
- Earache
- Electrocardiogram
- Enlarged adenoids
- Epilepsy
- Essential hypertension
- External rotation with band
- Fibromyalgia
- Flu
- Food poisoning
- Foot pain
- Gallstones
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Gastroesophageal reflux in ...
- Getting rid of lice in the home
- Glaucoma
- Hardening of arteries
- HbA1c
- Head injury
- Head lice
- Hearing loss
- Heartburn
- Heel pain
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hernia
- Herniated disk
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- How do ear tubes come out?
- How to remove a splinter
- How to stop bedwetting
- How to treat a nosebleed
- How to treat a sunburn
- How to use a peak flow meter
- How to use a pill cutter
- How to use eye drops
- How to use nasal sprays
- Hypertension
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Infant formulas
- Inguinal hernia repair
- Insomnia
- Internal rotation with band
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Isometric
- Kidney stones
- Let's talk about pink eye
- Lyme disease
- Lymph nodes
- Migraine
- Nasal congestion
- Neck pain
- Newborn jaundice
- NICU consultants and suppor...
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Pendulum exercise
- Pharyngitis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Pneumonia
- Prepare for your child's ea...
- Prepare for your child's he...
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff problems
- Scoliosis
- Seizures
- Shingles
- Shoulder blade retraction
- Shoulder blade retraction w...
- Shoulder pain
- Sinusitis
- Sleep disorders
- Stent
- Stomach ulcer
- Strep throat
- Stretching back of your shoulder
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Tension headache
- The difference between a co...
- Tips on buying cold and flu...
- Tips on removing ear wax
- Tonsillectomy
- Tonsillitis
- Treating congestion in babies
- Treating eyelid bumps
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Ulcerative colitis
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Up the back stretch
- Vacation health care
- Vaccines
- Varicose veins
- Wall push-up
- Wall stretch
- Warts
- What are hives?
- What are night terrors?
- What causes wheezing?
- What in the world is a neti pot?
- What is tennis elbow?
- What makes your heart beat?
- What to do when kids put th...
- What to do when kids put th...
- What to do when something g...
Illustrations
- Abdominal muscles
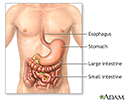
- Abdominal organs
- Abdominal quadrants
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Absence of menstruation (am...
- Absent pulmonary valve
- Acne - close-up of cysts on...
- Acne - close-up of pustular...
- Acne - cystic on the back
- Acne - cystic on the chest
- Acne - cystic on the face
- Acne - vulgaris on the back
- Acne on the back
- Acrodermatitis
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia ...
- Acute MI
- Adenocarcinoma - chest x-ray
- Adenoids
- Adjustable gastric banding
- Adolescent control test
- Adolescent pregnancy
- Adrenal glands
- AIDS
- Airway burn
- Aldosterone level test
- Allergic reactions
- Allergic reactions
- Allergic rhinitis
- Allergies
- Allergy skin prick or scrat...
- Allergy symptoms
- Alopecia areata with pustules
- Alopecia totalis - back vie...
- Alopecia totalis - front vi...
- Alopecia, under treatment
- Amino acids
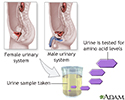
- Aminoaciduria urine test
- Anaphylaxis
- Anatomical landmarks adult ...
- Animal bite
- Animal bites
- Anomalous left coronary artery
- Anorectal fistulas
- Anterior skeletal anatomy
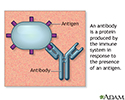
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Aortic rupture - chest x-ray
- Aortic stenosis
- Aortopulmonary window
- Apnea monitor
- Appendicitis
- Appendix
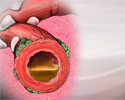
- Arterial plaque build-up
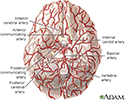
- Arteries of the brain
- Asthma
- Atherosclerosis of internal...
- Athlete's foot - tinea pedis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Atopy on the ankles
- Atrial septal defect
- Atrioventricular block - EC...
- Atrioventricular canal (end...
- Auer rods
- Auscultation
- Baby acne
- Baby bottle tooth decay
- Baby burping position
- Baby spitting up
- Bacteria
- Balance receptors
- Bananas and nausea
- Barium enema
- Basophil (close-up)
- Battle's sign - behind the ear
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Bedbug - close-up
- Bee sting
- Before and after small inte...
- Before and after testicular...
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Bicycle helmet - proper usage
- Bile produced in the liver
- Bili lights
- Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD)
- Black hairy tongue
- Black hairy tongue
- Black widow spider
- Black widow spider
- Blackheads (comedones)
- Blackheads (comedones) close-up
- Bladder catheterization - female
- Bladder catheterization - male
- Blocked tear duct
- Blood cells
- Blood clot formation
- Blood clots
- Blood pressure
- Blood pressure check
- Blood supply to bone
- Blood test
- Body louse
- Body louse, female and larvae
- Bone biopsy
- Bone bruise
- Bone marrow aspiration
- Bone marrow from hip
- Bone tumor
- Bowed chest (pigeon breast)
- Bradycardia
- Brain
- Brain structures
- Brain wave monitor
- Brainstem function
- Brain-thyroid link
- Breastfeeding
- Breath sounds
- Breathing
- Broad nasal bridge
- Bronchial cancer - chest x-ray
- Bronchiolitis
- Bronchitis
- Bronchitis and normal condi...
- Bronchoscopy
- Brown recluse spider
- Brown recluse spider bite o...
- Brudzinski's sign of meningitis
- Bulging fontanelles
- Burn, blister - close-up
- Burn, thermal - close-up
- Burns
- Calcium source
- Calories and fat per serving
- Campylobacter jejuni organism
- Candida - fluorescent stain
- Candidal esophagitis
- Canker sore
- Canker sore (aphthous ulcer)
- Capillary sample
- Caput succedaneum
- Cardiac arteriogram
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac catheterization
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Cataract
- Cataract
- Cataract - close-up of the eye
- Causes of acute bronchitis
- Causes of chronic bronchitis
- Causes of secondary headache
- Celiac sprue - foods to avoid
- Cellulitis
- Cellulitis on the arm
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system and ...
- Central venous catheter
- Cerebellum - function
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Check airway
- Chickenpox
- Chickenpox - close-up
- Chickenpox - lesion on the leg
- Chickenpox - lesions on the...
- Chickenpox, acute pneumonia...
- Chigger bite - close-up of ...
- Childhood obesity
- Cholelithiasis
- Cholesterol
- Chromosomes and DNA
- Chronic hepatitis
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia...
- Circulation of lymph
- Circulatory system
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Claw foot
- Claw hand
- Clostridioides difficile or...
- Clubbed fingers
- Clubbing
- Clubfoot deformity
- CMV (cytomegalovirus)
- CMV esophagitis
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Coccidioidomycosis - chest x-ray
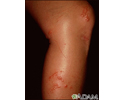
- Cold symptoms
- Collapsed lung, pneumothorax
- Colonoscopy
- Common asthma triggers
- Concussion
- Conduction system of the heart
- Congenital cytomegalovirus
- Congenital herpes
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Congenital nevus on the abdomen
- Congenital toxoplasmosis
- Conjunctivitis
- Cor pulmonale
- Coronary angiography
- Coronary artery blockage
- Coronary artery fistula
- Coronary artery stent
- Corpus callosum of the brain
- Cow's milk and children
- Crab lice
- Crab louse, female
- Craniotomy for cerebral shunt
- Cricoid cartilage
- Crohn disease - affected areas
- Crohn disease - X-ray
- Crossed eyes
- Crying - excessive (0 to 6 ...
- Cryptosporidium - organism
- CSF chemistry
- CT scan
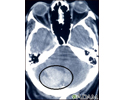
- CT scan of the brain
- Cutaneous anthrax
- Cutis marmorata on the leg
- Cyanosis of the nail bed
- Cyanotic heart disease
- Cyanotic 'Tet spell'
- Cystic fibrosis
- Cystoscopy
- DASH diet
- Deep venous thrombosis - il...
- Deer and dog tick
- Deer ticks
- Dental anatomy
- Depressed nasal bridge
- Depression in children
- Dermatitis - atopic in an infant
- Dermatitis - atopic on a yo...
- Dermatitis - atopic on the arms
- Dermatitis - atopic on the legs
- Dermatitis - close-up of al...
- Dermatitis - contact
- Dermatitis - contact on the...
- Dermatitis - herpetiformis ...
- Dermatitis - herpetiformis ...
- Dermatitis - pustular contact
- Dermatitis - seborrheic on ...
- Dermatitis seborrheic - close-up
- Dermatitis, nickel on the sole
- Dermatographism - arm
- Dermatographism - close-up
- Dermatographism on the arm
- Dermatographism on the back
- Detached retina
- Development of baby teeth
- Development of permanent teeth
- Developmental disorders of ...
- Developmental disorders of ...
- Developmental growth
- Developmental milestones
- Dextrocardia
- Diabetes and exercise
- Diabetic blood circulation ...
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Diaper rash
- Diapers and diarrhea
- Diaphragm
- Diaphragm and lungs
- Diarrhea
- Diastasis recti
- Diet and good health
- Different types of weight gain
- Digestive system
- Digestive system organs
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Dislocation of the hip
- Double aortic arch
- Double inlet left ventricle
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Drooling
- Dust mite
- Dust mite-proof pillow cover
- Ear abnormalities
- Ear anatomy
- Ear drainage culture
- Early treatment of injury
- Ebstein's anomaly
- ECG
- ECHO virus type 9 - exanthem
- ECMO
- Eczema, atopic - close-up
- Eisenmenger syndrome (or co...
- Electrical injury
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Emergency airway puncture
- Emphysema
- Endocrine glands
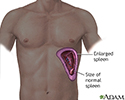
- Enlarged spleen
- Eosinophilic granuloma - x-...
- Epicanthal fold
- Epicanthal folds
- Epidermolysis bullosa, domi...
- Epidermolysis bullosa, dyst...
- Epiglottis
- ERCP
- Erythema annulare centrifug...
- Erythema multiforme on the leg
- Erythema multiforme, circul...
- Erythema multiforme, target...
- Erythema nodosum associated...
- Erythema toxicum neonatorum...
- Erythema toxicum on the foot
- Erythroblastosis fetalis - ...
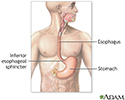
- Esophagus
- Esophagus and stomach anatomy
- Eustachian tube
- Ewing sarcoma - x-ray
- Exercise - dress appropriately
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- Exercise-induced asthma
- External and internal ear
- External and internal eye a...
- External fixation device
- Eye
- Eye redness
- Fecal occult blood test
- Feeding tube
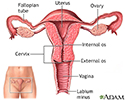
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy...
- Female urinary tract
- Femoral fracture
- Fetal alcohol syndrome
- Fetal head molding
- Fifth disease
- Fire safe home
- First aid kit
- First degree burn
- Fish in diet
- Flea
- Flea bite - close-up
- Fly
- Folic acid source
- Folliculitis - decalvans on...
- Folliculitis on the leg
- Fontanelles
- Food allergies
- Food and insulin release
- Food poisoning
- Foreign object in ear
- Foreign object removal
- Foreskin
- Formed elements of blood
- Forward bend test
- Forward-facing car seat
- Fracture types (1)
- Fracture types (2)
- Fracture, forearm - x-ray
- Fractured clavicle (infant)
- Fractures across a growth plate
- Frontal bossing
- Frostbite
- Frostbite - hands
- Fruits and vegetables
- Fungus
- Galactosemia
- Gallstones
- Gastric endoscopy
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Gaucher cell - photomicrograph
- Gaucher cell - photomicrogr...
- Gestational ages
- Gianotti-Crosti syndrome on...
- Giardiasis
- Gingivitis
- Gingivitis
- Glaucoma
- Glucose in blood
- Glucose test
- Goiter
- Gonadotropins
- Grand mal seizure
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Graves disease
- Haemophilus influenza organism
- Haemophilus influenzae organism
- Hair follicle sebaceous gland
- Hammer toe
- Hand, foot, and mouth disea...
- Hand, foot, and mouth disea...
- Hand, foot, and mouth disea...
- Hand, foot, and mouth disea...
- Hand, foot, and mouth disea...
- Hand-foot-mouth disease
- Hanta virus
- Hashimoto's disease (chroni...
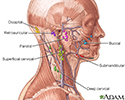
- Head and neck glands
- Head circumference
- Head injury
- Head lice
- Head louse - female
- Head louse and pubic louse
- Head louse emerging from egg
- Head louse infestation - scalp
- Head louse, male
- Headache
- Healthy diet
- Hearing test
- Heart - front view
- Heart - respiratory monitor
- Heart - section through the...
- Heart valves
- Heart valves - anterior view
- Heart valves - superior view
- Heartburn prevention
- Heat emergencies
- Heat rash
- Height/weight chart
- Heimlich maneuver on adult
- Heimlich maneuver on an adult
- Heimlich maneuver on consci...
- Heimlich maneuver on consci...
- Heimlich maneuver on infant
- Heimlich maneuver on infant
- Heimlich maneuver on infant
- Heimlich maneuver on oneself
- Hemangioma - angiogram
- Hemangioma on the chin
- Hemangioma on the face (nose)
- Hemoglobin
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura on...
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura on...
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura on...
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura on...
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura on...
- HEPA air filter
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis A immunization (v...
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Herniated lumbar disk
- Herpes zoster (shingles) di...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpetic esophagitis
- Hiatal hernia
- Hiatal hernia - x-ray
- Hib immunization (vaccine)
- High blood pressure tests
- Histamine is released
- Histoplasmosis, disseminate...
- HIV
- Hives
- Hives (urticaria) - close-up
- Hives (urticaria) - close-up
- Hives (urticaria) on the arm
- Hives (urticaria) on the back
- Hives (urticaria) on the ba...
- Hives (urticaria) on the chest
- Hives (urticaria) on the chest
- Hives (urticaria) on the trunk
- Hodgkin's disease - liver i...
- Home safety
- Hormonal effects in newborns
- Humidifiers and health
- Hunger center in brain
- Hydrocele
- Hydrops fetalis
- Hyperglycemia
- Hyperlinearity in atopic de...
- Hyperlinearity in atopic de...
- Hypermobile joints
- Hyperpigmentation 2
- Hypersegmented PMN (Close-up)
- Hypertension
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypospadias
- Hypothalamus
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypotonia
- Ileus - x-ray of bowel dist...
- Ileus - x-ray of distended ...
- Immune system structures
- Immunizations
- Immunizations
- Immunizations
- Imperforate anus
- Impetigo - bullous on the b...
- Impetigo on a child's face
- Incontinentia pigmenti - side
- Incontinentia pigmenti on t...
- Incontinentia pigmenti on t...
- Indications of head injury
- Infant abdominal hernia (ga...
- Infant blood sample
- Infant brain test
- Infant care following delivery
- Infant dental care
- Infant diaphragmatic hernia
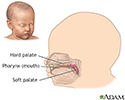
- Infant hard and soft palates
- Infant heat rash
- Infant immunizations
- Infant intestines
- Infant jaundice
- Infant omphalocele
- Infant skull fracture
- Infant test/procedure prepa...
- Infantile reflexes
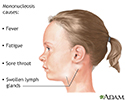
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Infectious mononucleosis #3
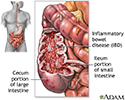
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Influenza
- Influenza
- Influenza vaccines
- Ingrown toenail
- Inguinal hernia
- Inhalation Anthrax
- Inhaler medication administ...
- Insect bite reaction - close-up
- Insect bites and stings
- Insect bites on the legs
- Insect stings and allergy
- Institutional hygiene
- Insulin production and diabetes
- Insulin pump
- Insulin pump
- Internal fixation devices
- Intervertebral disk
- Intestinal gas
- Intracerebellar hemorrhage ...
- Intradermal allergy test re...
- Intravenous fluid sites
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- Introduction to allergy tre...
- Intussusception - x-ray
- Irregular sleep
- Islets of Langerhans
- Janeway lesion on the finger
- Jaundiced infant
- Kaposi sarcoma - close-up
- Kaposi sarcoma - lesion on ...
- Kaposi sarcoma on the back
- Kaposi's sarcoma on the thigh
- Karyotyping
- Kawasaki disease - edema of...
- Kawasaki's disease - peelin...
- Keratosis pilaris - close-up
- Keratosis pilaris on the cheek
- Kernicterus
- Kernig's sign of meningitis
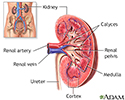
- Kidney anatomy
- Kidney function
- Kissing bug
- Kwashiorkor symptoms
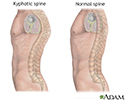
- Kyphosis
- Laceration versus puncture wound
- Large fontanelles
- Large fontanelles (lateral view)
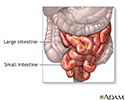
- Large intestine
- Large intestine (colon)
- Latex allergy
- Left cerebral hemisphere - ...
- Left heart catheterization
- Leg pain (Osgood-Schlatter)
- Lice, body with stool (Pedi...
- Lice, head - nits in the ha...
- Lifestyle changes
- Limbic system
- Lipocytes (fat cells)
- Lipoma - arm
- Liver biopsy
- Lordosis
- Low blood sugar symptoms
- Lower digestive anatomy
- Lower leg muscles
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
- Lumbar vertebrae
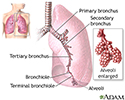
- Lung anatomy
- Lung cancer - frontal chest...
- Lung mass, right upper lung...
- Lung nodule - front view ch...
- Lung nodule, right middle l...
- Lungs
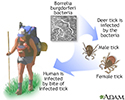
- Lyme disease
- Lyme disease - Borrelia bur...
- Lymph tissue in the head an...
- Lymphangiogram
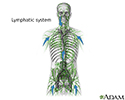
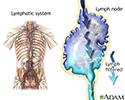
- Lymphatic system
- Lymphatic system
- Macular degeneration
- Malaria, microscopic view o...
- Malaria, photomicrograph of...
- Male and female reproductiv...
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male reproductive hygiene
- Male reproductive system
- Male urinary tract
- Malignant teratoma
- Malocclusion of teeth
- Marfan syndrome
- Mastocytosis - diffuse cutaneous
- Mastoiditis - redness and s...
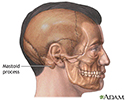
- Mastoiditis - side view of head
- Match test
- Measles on the back
- Measles, Koplik spots - close-up
- Meatal stenosis
- Meconium
- Medical findings based on e...
- Megaloblastic anemia - view...
- Meninges of the brain
- Meninges of the spine
- Meningococcal lesions on th...
- Meningococcemia associated ...
- Meningococcemia on the calves
- Meningococcemia on the leg
- Meniscal tears
- Metatarsus adductus
- Metopic ridge
- Microcephaly
- Microscopic polyarteritis 2
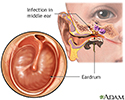
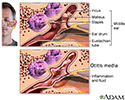
- Middle ear infection
- Middle ear infection (otiti...
- Migraine headache
- Milia - nose
- Miliaria crystallina - ches...
- Miliaria crystallina - ches...
- Miliaria crystallina - close-up
- Miliaria profunda - close-up
- Miliary tuberculosis
- Molluscum - microscopic app...
- Molluscum contagiosum - close-up
- Molluscum contagiosum - clo...
- Molluscum contagiosum on th...
- Molluscum on the chest
- Mongolian blue spots
- Monitoring blood pressure
- Mononucleosis - mouth
- Mononucleosis - photomicrog...
- Mononucleosis - photomicrog...
- Mononucleosis - photomicrog...
- Mononucleosis - view of the...
- Moro reflex
- Mosquito, adult
- Mosquito, adult feeding on ...
- Mosquito, egg raft
- Mosquito, pupa
- Motormental disability
- Mouth anatomy
- Mouth sores
- MRI scans
- Muscle bruise
- Muscle cells vs. fat cells
- Muscle strain
- Muscular atrophy
- Mycobacterium marinum infec...
- Myocarditis
- myPlate
- Nailcare for newborns
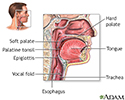
- Nasal anatomy
- Nasal CPAP
- Nasal flaring
- Nasal mucosa
- Nasal polyps
- Nasal spray flu vaccine
- Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy
- Neonate
- Nephrolithiasis
- Neuroblastoma in the liver ...
- Newborn ear anatomy
- Newborn head molding
- Newborn screening testing
- Newborn test
- Nit on human hair
- Normal heart rhythm
- Normal lung anatomy
- Normal lungs and alveoli
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Normal versus asthmatic bro...
- Normal vision
- Normal, nearsightedness, an...
- Nosebleed
- Obesity and health
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Optic nerve
- Oral anatomy
- Oral thrush
- Oropharynx
- Osteogenic sarcoma - x-ray
- Otoscope examination
- Otoscopic exam of the ear
- Ovalocytosis
- Pacemaker
- Pain medications
- Palpebral slant
- Pancreas
- Pancreas
- Pancreatitis, acute - CT scan
- Pancreatitis, chronic - CT scan
- Patent urachus
- Peak flow meter
- Pectus excavatum
- Penis - with and without fo...
- Perioral dermatitis
- Periorbital cellulitis
- Peristalsis
- Phagocytosis
- Phenylketonuria test
- Photocontact dermatitis on ...
- Phytochemicals
- Pinna of the newborn ear
- Pinworm - close-up of the head
- Pinworms
- Pituitary and TSH
- Pituitary gland
- Plantar wart
- Pneumococcal pneumonia
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Pneumococci organism
- Pneumonia
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumothorax - chest x-ray
- Poison control center - Eme...
- Poison ivy on the knee
- Poison ivy on the leg
- Poison oak rash on the arm
- Poison plants
- Poliomyelitis
- Polyarteritis - microscopic...
- Polydactyly - an infant's hand
- Port wine stain on a child'...
- Positive PPD skin test
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigm...
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigm...
- Postural drainage
- PPD skin test
- Preschooler development
- Preschooler test
- Prevention of cystitis
- Primary amenorrhea
- Primary brain tumor
- Primary HIV infection
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Primary syphilis
- Prognathism
- Psoriasis - guttate on the ...
- Psoriasis - guttate on the cheek
- Psoriasis on the knuckles
- Ptosis - drooping of the eyelid
- Pubic louse-male
- Pulmonary embolus
- Pulmonary mass - side view ...
- Pulmonary nodule - front vi...
- Pulmonary nodule, solitary ...
- Pyloric stenosis
- Rabies
- Rabies
- Radial head injury
- Rash
- RAST test
- Read food labels
- Rear-facing car seat
- Recognizing invader
- Rectum
- Red blood cells - elliptocytosis
- Red blood cells - multiple ...
- Red blood cells - normal
- Red blood cells - sickle an...
- Red blood cells - sickle cells
- Red blood cells - spherocytosis
- Red blood cells, sickle cell
- Red blood cells, target cells
- Red blood cells, tear-drop shape
- Respiratory system
- Respiratory system overview
- Retina
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ribcage
- Right cerebral hemisphere -...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea manuum on ...
- Ringworm - tinea on the han...
- Ringworm, tinea capitis - c...
- Rocky mountain spotted feve...
- Role of the vagus nerve in ...
- Roseola
- Roux-en-Y stomach surgery f...
- Rubella
- Rubella on an infant's back
- Rubella syndrome
- Runny and stuffy nose
- Ruptured eardrum
- Sacrum
- Salmonella typhi organism
- Sarcoid - close-up of the s...
- Sarcoid, stage I - chest x-ray
- Sarcoid, stage II - chest x-ray
- Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray
- Sarcoidosis - close-up
- Sarcoidosis on the elbow
- Sarcoidosis on the nose and...
- Scabies mite - photomicrograph
- Scabies mite - photomicrograph
- Scabies mite - photomicrograph
- Scabies mite - photomicrogr...
- Scabies mite, eggs, and sto...
- Scabies rash and excoriatio...
- Schatzki ring - x-ray
- School age child development
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis brace
- Second degree burn
- Secondary amenorrhea
- Sense of hearing
- Sense of smell
- Shaken baby symptoms
- Shingles
- Shock
- Shoulder joint
- Side sectional view of fema...
- Signs of drug use
- Signs of scarlet fever
- Signs of scoliosis
- Single palmar crease
- Sinuses
- Sinusitis
- Skeletal spine
- Skeleton
- Skin
- Skin bruise
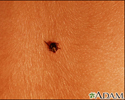
- Skin cancer, melanoma on th...
- Skin characteristics
- Skin layers
- Skin testing - PPD (R arm) ...
- Skin turgor
- Skull fracture
- Skull fracture
- Skull of a newborn
- Sleep patterns in the young...
- Slit-lamp exam
- Small bowel obstruction - x-ray
- Small intestine
- Smashed fingers
- Snake bite
- Sound wave transmission
- Sources of fiber
- Spina bifida
- Spina bifida (degrees of se...
- Spinal anatomy
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal curves
- Spinal fusion
- Spinal stenosis
- Spirometry
- Spitting up
- Splenomegaly
- Sponge bath
- STDs and ecological niches
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Stinger removal
- Stitches
- Stomach
- Stomach and small intestine
- Stomach disease or trauma
- Stopping bleeding with a to...
- Stopping bleeding with dire...
- Stopping bleeding with pres...
- Stork bite
- Strep throat
- Stroke
- Structure of the colon
- Sturge-Weber syndrome - legs
- Stye
- Substance use during pregnancy
- Subungual wart
- Sun protection
- Sunburn
- Sunken fontanelles (superio...
- Superficial anterior muscles
- Supernumerary nipple
- Supernumerary nipples
- Support group counselors
- Swan Ganz catheterization
- Sweat test
- Sweat test
- Swimmer's ear
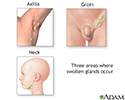
- Swollen glands
- Swollen gums
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin
- Syndactyly
- Systemic lupus erythematosu...
- Teach children to brush
- Teenage depression
- Teething symptoms
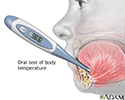
- Temperature measurement
- Tension-type headache
- Teratoma - MRI scan
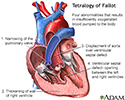
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Thalassemia major
- Thalassemia minor
- The face
- The skeleton (lateral view)
- Thermometer temperature
- Third degree burn
- Throat anatomy
- Thrombus
- Thumbsucking
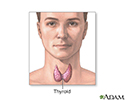
- Thyroid gland
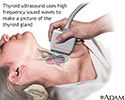
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Tick - deer engorged on the skin
- Tick imbedded in the skin
- Tick, deer - adult female
- Ticks
- Time out
- Tinea (ringworm)
- Tinea corporis - ear
- Tinea versicolor - back
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - shoulders
- Tinea versicolor on the back
- Toddler development
- Toddler test
- Tonsillectomy
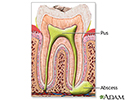
- Tooth abscess
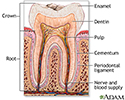
- Tooth anatomy
- Tooth anatomy
- Torticollis (wry neck)
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Transposition of the great ...
- Treatment for leg strain
- Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Tuberculosis of the lungs
- Tuberculosis, advanced - ch...
- TV watching
- Tympanic membrane
- Type I diabetes
- Ulcer emergencies
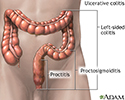
- Ulcerative colitis
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
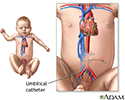
- Umbilical catheter
- Umbilical cord healing
- Umbilical hernia
- Untreated hypertension
- Upper gastrointestinal system
- Ureterocele
- Urticaria pigmentosa - close-up
- Urticaria pigmentosa in the...
- Urticaria pigmentosa on the...
- Uterus
- Vascular headaches
- Vascular ring
- Venous blood clot
- Ventricles of the brain
- Ventricular septal defect
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Vertebra, cervical (neck)
- Vertebra, lumbar (low back)
- Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
- Vertebrae
- Vertebral column
- Vertical banded gastroplasty
- Vertigo
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Visual acuity test
- Visual field test
- Vitamin A source
- Vitamin B12 source
- Vitamin B6 source
- Vitamin C benefit
- Vitamin C source
- Vitamin D source
- Vitiligo - drug induced
- Vitiligo on the back and arm
- Vitiligo on the face
- Voice box
- Voiding cystourethrogram
- Volvulus - x-ray
- Walleyes
- Wart
- Wart (close-up)
- Wart (verruca) with a cutan...
- Warts - flat on the cheek a...
- Wasp
- Weight loss
- White nail syndrome
- Wilms tumor
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-ray
- Yeast and mold
- Yersinia enterocolitica organism
- Yoga
- Yo-yo dieting
Presentations
- Achalasia - series
- Adenoid removal - series
- Animal bite - first aid - series
- Ankle sprain - Series
- Appendectomy - series
- Bone fracture repair - series
- Bone-marrow transplant - series
- Bruise healing - series
- Cataract surgery - series
- Chest tube insertion - series
- Choking first aid - adult o...
- Choking first aid - infant ...
- Circumcision - series
- Cleft lip repair - series
- Clubfoot repair - series
- Colon cancer - series
- Complete blood count - series
- Convulsions - first aid - series
- CPR - child 1 to 8 years ol...
- CPR - infant - series
- Craniotomy - series
- Diaphragmatic hernia repair...
- Ear tube insertion - series
- Eardrum repair - series
- Emergency airway puncture ...
- Exchange transfusion - series
- Gastroesophageal reflux - series
- Gastroschisis repair - series
- Heart valve surgery - series
- Hemangioma excision - series
- Hiatal hernia repair - series
- Hydrocele repair - series
- Hypospadias repair - series
- Imperforate anus repair - ...
- Infantile pyloric stenosis ...
- Inflammatory bowel disease ...
- Inguinal hernia repair - series
- Intestinal obstruction (ped...
- Intestinal obstruction repa...
- Large bowel resection - series
- Leg lengthening - series
- Mastoidectomy - series
- Meckel's diverticulectomy ...
- Meningocele repair - series
- Metered dose inhaler use - ...
- Minor burn - first aid - series
- Minor cut - first aid
- Monitoring blood glucose - ...
- Nebulizer use - series
- Omphalocele repair - series
- Pancreatitis - series
- Patent ductus arteriosis (P...
- Patent urachus repair - series
- Pectus excavatum repair - ...
- Pneumothorax - series
- Repair of webbed fingers -...
- Retinal detachment repair ...
- Small bowel resection - series
- Spleen removal - series
- Thyroidectomy - series
- Tonsillectomy - series
- Tracheoesophageal fistula r...
- Two person roll - series
- Umbilical hernia repair - ...
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt ...
- White blood cell count - series

 Bookmark
Bookmark