Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency

Definition
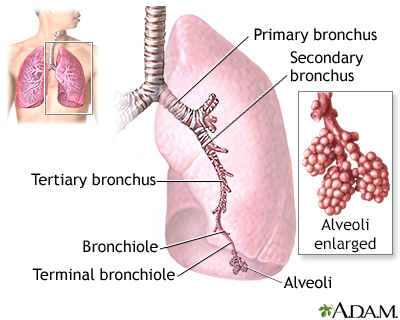
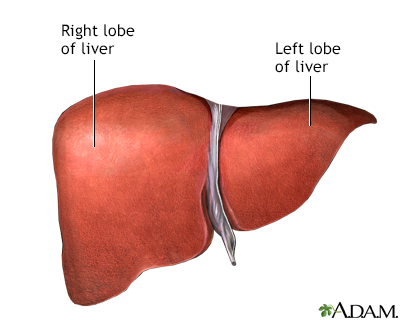
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency is a condition in which the body does not make enough of AAT, a protein that protects the lungs and liver from damage. The condition can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and liver disease (cirrhosis).
Causes
AAT is a type of protein called a protease inhibitor. AAT is made in the liver and it works to protect the lungs and liver.
AAT deficiency means there is not enough of this protein in the body. It is caused by a genetic variant. The condition is most common among Europeans and North Americans of European descent.
Adults with severe AAT deficiency will develop emphysema, sometimes before 40 years of age. Smoking can increase the risk for emphysema and make it occur earlier.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Shortness of breath with and without exertion, and other symptoms of COPD
- Symptoms of liver failure
- Loss of weight without trying
- Wheezing
- Coughing
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may reveal a barrel-shaped chest, wheezing, or decreased breath sounds. The following tests may also help with diagnosis:
- AAT blood test
- Arterial blood gases
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the chest
- Genetic testing
- Lung function tests
Your health care provider may suspect you of having this condition if you develop:
- COPD before age 45
- COPD but you have never smoked or been exposed to toxins
- COPD and you have a family history of the condition
- Cirrhosis and no other cause can be found
- Cirrhosis and you have a family history of liver disease
Treatment
Treatment for AAT deficiency involves replacing the missing AAT protein. The protein is given through a vein each week or every 4 weeks. This is only slightly effective at preventing more lung damage in people without end-stage disease. This procedure is called augmentation therapy.
If you smoke, you need to quit.
Other treatments are also used for COPD and cirrhosis.
Lung transplant can be used for severe lung disease, and liver transplant can be used for severe cirrhosis.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Some people with this deficiency will not develop liver or lung disease. If you quit smoking, you can slow the progression of the lung disease.
COPD and cirrhosis can be life threatening.
Possible Complications
Complications of AAT deficiency include:
- Bronchiectasis (damage of the large airways)
- COPD
- Liver failure or cancer
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of AAT deficiency.
References
Han MK, Lazarus SC. COPD: diagnosis and management. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 64.
Masson VK, Boas SR. a1 -antitrypsin deficiency and emphysema. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 442.
Tejwani V, Stoller JK. The spectrum of clinical sequelae associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021;12_suppl. PMID: 34408829 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34408829/.
Review Date: 8/19/2024
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.