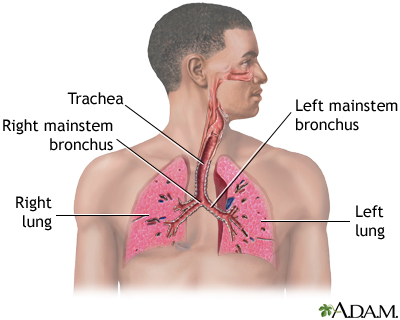
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lung and right ventricle of the heart can lead to cor pulmonale.
Causes
High blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs is called pulmonary hypertension. It is the most common cause of cor pulmonale.
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...

Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
In people who have pulmonary hypertension, changes in the small blood vessels inside the lungs can lead to increased blood pressure in the right side of the heart. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the lungs. If this high pressure continues, it puts a strain on the right side of the heart. That strain can cause cor pulmonale.
Lung conditions that cause a low blood oxygen level in the blood over a long time can also lead to cor pulmonale. Some of these are:
- Autoimmune diseases that damage the lungs, such as scleroderma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Chronic blood clots in the lungs
- Cystic fibrosis (CF)
- Severe bronchiectasis
- Scarring of the lung tissue (interstitial lung disease)
- Severe curving of the upper part of the spine (kyphoscoliosis)
- Obstructive sleep apnea, which causes stops in breathing during sleep
Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a problem in which your breathing pauses during sleep. This occurs because of narrowed or blocked airways.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Idiopathic (no specific cause) tightening (constriction) of the blood vessels of the lungs, also called primary pulmonary hypertension
- Severe left-sided heart failure
Symptoms
Shortness of breath or lightheadedness during activity is often the first symptom of cor pulmonale. You may also have a fast heartbeat and feel like your heart is pounding.
Over time, symptoms occur with lighter activity or even while you are at rest. Symptoms you may have are:
- Fainting spells during activity
- Chest discomfort, usually in the front of the chest
- Chest pain
- Swelling of the feet or ankles
- Symptoms of lung disorders, such as wheezing or coughing or phlegm production
- Bluish lips and fingers (cyanosis)
Bluish lips and fingers
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. The exam may find:
- Fluid buildup in your belly
- Abnormal heart sounds
- Bluish skin
- Liver swelling
- Swelling of the neck veins, which is a sign of high pressure in the right side of the heart
- Ankle swelling
These tests may help diagnose cor pulmonale as well as its cause:
- Blood antibody tests
- Blood test to check for a substance called brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
Brain natriuretic peptide
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) test is a blood test that measures levels of the protein BNP that is made by your heart and blood vessels. BNP level...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
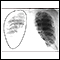
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of the chest, with or without an injection of a contrast fluid (dye)
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung biopsy (rarely done)
- Measurement of blood oxygen by checking arterial blood gas (ABG)
Arterial blood gas
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary (lung) function tests
- Right heart catheterization
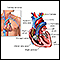
Right heart catheterization
Swan-Ganz catheterization (also called right heart catheterization or pulmonary artery catheterization) is the passing of a thin tube (catheter) into...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ventilation and perfusion scan of the lungs (V/Q scan)
Ventilation and perfusion scan of the l...
A pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan involves two nuclear scan tests to measure breathing (ventilation) and circulation (perfusion) in all areas of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tests for autoimmune lung disease
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to control symptoms. It is important to treat medical problems that cause pulmonary hypertension, because they can lead to cor pulmonale.
Many treatment options are available. In general, the cause of your cor pulmonale will determine which treatment you receive.
If your provider prescribes medicines, you may take them by mouth (oral), receive them through a vein (intravenous or IV), or breathe them in (inhaled). You will be closely monitored during treatment to watch for side effects and to see how well the medicine works for you. Never stop taking your medicines without first talking to your provider.
Other treatments may include:
- Blood thinners to reduce the risk of blood clots
- Medicines to manage heart failure symptoms
Medicines to manage heart failure sympt...
Most people who have heart failure need to take medicines. Some of these medicines are used to treat your symptoms. Others may help prevent your he...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Oxygen therapy at home (as in most cases of cor pulmonale, oxygen is low)
- A lung or heart-lung transplant, if medicine does not work
Important tips to follow:
- Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting.
- Avoid traveling to high altitudes.
- Get a yearly flu vaccine, as well as other vaccines, such as the pneumococcal (pneumonia) vaccine, and the COVID-19 vaccine.
- If you smoke, stop.
Smoke, stop
There are many ways to quit smoking. There are also resources to help you. Family members, friends, and co-workers may be supportive. But to be su...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Limit how much salt you eat. Your provider also may ask you to limit how much fluid you drink during the day.
- Use oxygen if your provider prescribes it.
- Women should not get pregnant.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on the cause of your cor pulmonale.
As your illness gets worse, you will need to make changes to your home so that you can manage as well as possible. You will also need help around your house.
Possible Complications
Cor pulmonale may lead to:
- Life-threatening shortness of breath
- Severe fluid buildup in your body
- Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have shortness of breath or chest pain.
Prevention
Do not smoke. Smoking causes lung disease, which can lead to cor pulmonale.
Reviewed By
Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Lammi MR, Mathai SC. Pulmonary hypertension: general approach. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 83.
Maron B. Pulmonary hypertension. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.