Multimedia Gallery
Hardening of arteries
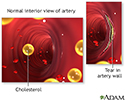
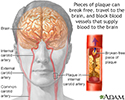
Blood is the fuel that keeps your body alive and working. It's your blood that transports the oxygen your cells need to survive. To get to your heart and out the rest of your body, blood needs a clear pathway through your arteries. But as you get older and if you eat too many French fries and cheeseburgers your arteries can harden and narrow, fill with plaque leaving less room for blood to flow through.
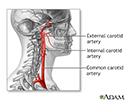
Let's talk today about atherosclerosis. Your arteries are like the pipes your water flows through to get to your bathroom sink. When the pipes are clear, water flows easily through them. But when rust, minerals, and other debris get stuck in the pipes, it clogs them up, leaving less room for water to flow through. That's why you get nothing more than a drip when you turn on your bathroom sink. In your arteries, clogs are caused by plaque. Plaque is a substance made up of fat and cholesterol which are found in unhealthy food like those French fries and also bacon. Because plaque is sticky it collects on your artery walls and blocks the flow of blood. Sometimes a clump of plaque breaks off and floats away to a smaller blood vessel leading to your heart or brain. If it gets stuck in that vessel, you can have a heart attack or a stroke. Or, the plaque can weaken an artery wall which is called an aneurysm. If that aneurysm breaks open, you could have a very life threatening bleeding.
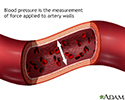
How can you tell if you have atherosclerosis? Well, that's the tricky part because often atherosclerosis doesn't cause any symptoms until you've got a blocked artery. And by then, you could already be having a heart attack or stroke. So that you don't discover the problem too late, see your doctor for regular check-ups. Get your cholesterol screened by age 35 if you're a man, age 45 if you're a women. Also, have your blood pressure checked every one to two years before age 50. And then once a year after that. You may need to have your blood pressure checked even more often if you have high blood pressure, heart disease, or if you have already had a stroke.
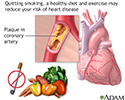
Although you can't reverse atherosclerosis once it starts, you can prevent it with some easy lifestyle changes. Eat a balanced diet that's high in heart healthy fruits, vegetables, and fish. Exercise for at least 30 to 60 minutes a day. Stop smoking because that's really bad news for your arteries. If your cholesterol is high, ask your doctor whether you should be taking cholesterol lowering medication. Lastly, you may also need to take aspirin or another blood thinning drug to prevent clots from forming in your arteries.
Hardening of arteries
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Animations
- Alzheimer disease
- Alzheimer disease
- Asperger syndrome
- Atherosclerosis
- Athetosis resulting from ba...
- Attention deficit hyperacti...
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Bladder function - neurolog...
- Brain components
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Cerebral palsy
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Cluster headache
- Concussion
- Concussion
- Diabetes
- Epilepsy
- Epinephrine and exercise
- Erection problems
- Essential hypertension
- Feeling pain
- Hardening of arteries
- Head injury
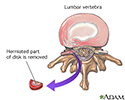
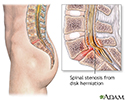
- Herniated disk
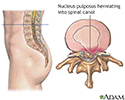
- Herniated nucleus pulposus ...
- How to use a pill cutter
- Hypertension - overview
- Insomnia
- Migraine
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neck pain
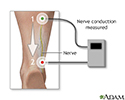
- Nerve conduction
- Parkinson disease
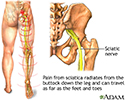
- Sciatica
- Seizures
- Shingles
- Sleep disorders
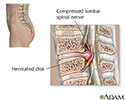
- Spinal stenosis
- Stroke
- Stroke
- Stroke - secondary to cardi...
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Tension headache
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Urinary incontinence
Illustrations
- 15/15 rule
- Active vs. inactive muscle
- Acupuncture
- Adult dermatome
- Alcoholic neuropathy
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Alzheimer disease
- Amebic brain abscess
- Amyloidosis of the fingers
- Arterial plaque build-up
- Arterial tear in internal c...
- Arteries of the brain
- Atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis of internal...
- Autonomic Nerves
- Balance receptors
- Before and after hematoma repair
- Bicycle helmet - proper usage
- Biguanides
- Blood pressure
- Blood pressure check
- Blood test
- Blood test
- Bone graft harvest
- Brain
- Brain
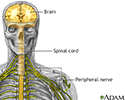
- Brain and nervous system
- Brain herniation
- Brain structures
- Brain wave monitor
- Brainstem function
- Brudzinski's sign of meningitis
- Calories and fat per serving
- Carotid dissection
- Carotid duplex
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carpal tunnel surgical procedure
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cataract - close-up of the eye
- Cauda equina
- Cause of headaches
- Causes of secondary headache
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cerebellum - function
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Cerebrospinal fluid leak
- Cervical spondylosis
- Cervical vertebrae
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol producers
- Circle of Willis
- Common peroneal nerve dysfu...
- Complex carbohydrates
- Compression fracture
- Compression of the median nerve
- Concussion
- Congenital toxoplasmosis
- Copper urine test
- Coronary artery blockage
- Craniotomy for cerebral shunt
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Crossed eyes
- CSF cell count
- CSF chemistry
- CSF protein test
- CT scan
- CT scan of the brain
- Damaged axillary nerve
- DASH diet
- Developmental process of at...
- Diabetes and exercise
- Diabetes and nerve damage
- Diabetic blood circulation ...
- Diabetic emergency supplies
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Ear anatomy
- Effects of age on blood pressure
- Electromyography
- Endarterectomy
- Endocrine glands
- Enlarged view of atherosclerosis
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- External and internal eye a...
- Eye
- Eye ultrasound
- Facial drooping
- Femoral nerve damage
- Fibromyalgia
- Fish in diet
- Food and insulin release
- Forward bend test
- Glaucoma
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Glucose in blood
- Glucose test
- Grand mal seizure
- Gray and white matter of th...
- Haemophilus influenzae organism
- Head injury
- Head trauma
- Headache
- Healthy diet
- Herniated disk repair
- Herniated lumbar disk
- Herniated nucleus pulposus
- Herpes zoster (shingles) - ...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) di...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- Herpes zoster (shingles) on...
- High blood pressure tests
- Hunger center in brain
- Hypothalamus
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Indications of head injury
- Insulin production and diabetes
- Insulin pump
- Insulin pump
- Intervertebral disk
- Intracerebellar hemorrhage ...
- Intracerebral hemorrhage
- Intracranial pressure monitoring
- Irregular sleep
- Kernig's sign of meningitis
- Kyphosis
- Late-stage syphilis
- Left cerebral hemisphere - ...
- Leukoencephalopathy
- Lifestyle changes
- Limbic system
- Lobes of the brain
- Location of whiplash pain
- Low blood sugar symptoms
- Lower leg muscles
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
- Lumbar vertebrae
- Lumbar vertebrae
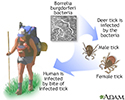
- Lyme disease
- Lyme disease - Borrelia bur...
- Lyme disease - erythema migrans
- Lyme disease organism - Bor...
- Meninges of the brain
- Meninges of the spine
- Migraine cause
- Migraine headache
- Monitoring blood pressure
- Motor nerves
- MRI of the brain
- MRI scans
- Multiple sclerosis
- Muscle cells vs. fat cells
- Muscle fatigue
- Muscle pain
- Muscular atrophy
- Myelin and nerve structure
- myPlate
- Neck pain
- Nerve biopsy
- Nerve conduction test
- Nerve supply to the pelvis
- Nervous system
- Neurofibromatosis I - enlar...
- Normal pupil
- Omega-3 fatty acids
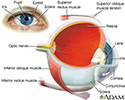
- Optic nerve
- Pain of cluster headache
- Phytochemicals
- Pituitary gland
- Plaque buildup in arteries
- Prevention of heart disease
- Primary brain tumor
- Ptosis - drooping of the eyelid
- Radial nerve dysfunction
- Radiation therapy
- Retina
- Right cerebral hemisphere -...
- Role of the vagus nerve in ...
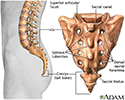
- Sacrum
- Saturated fats
- Sciatic nerve
- Sciatic nerve damage
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis brace
- Shaken baby symptoms
- Shingles
- Signs of scoliosis
- Simple carbohydrates
- Skeletal spine
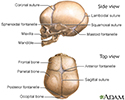
- Skull of a newborn
- Skull of an adult
- Sleep patterns in the young...
- Sleep studies
- Slit-lamp exam
- Soluble and insoluble fiber
- Spinal anatomy
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal curves
- Spinal fusion
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal tumor
- Spine supporting structures
- Stroke
- Subdural hematoma
- Subdural hematoma
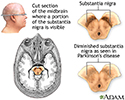
- Substantia nigra and Parkin...
- Sulfonylureas drug
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Tension-type headache
- Thiazolidinediones
- Thoracic outlet anatomy
- Tibial nerve
- Tick - deer engorged on the skin
- Tick, deer - adult female
- Torticollis (wry neck)
- Trans fatty acids
- Transient Ischemic attack (TIA)
- Tympanic membrane
- Type I diabetes
- Ulnar nerve damage
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Untreated hypertension
- Vascular headaches
- Ventricles of the brain
- Vertebra and spinal nerves
- Vertebra, cervical (neck)
- Vertebra, lumbar (low back)
- Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
- Vertebrae
- Vertebral column
- Vertigo
- Visual acuity test
- Visual field test
- Vitamin B6 benefit
- Vitamin B6 source
- Voiding cystourethrogram
- Weight loss
- Whiplash
- Wrist anatomy
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-linked recessive genetic ...
- X-ray
- Yo-yo dieting
Presentations
- Carotid artery surgery - series
- Carpal tunnel repair - series
- Craniotomy - series
- CSF oligoclonal banding - ...
- Lumbar spinal surgery - series
- Meningocele repair - series
- Microdiskectomy - series
- Monitoring blood glucose - ...
- Spinal fusion - series
- Spinal surgery - cervical -...
- Stroke - series
- Two person roll - series
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt ...

 Bookmark
Bookmark