Multimedia Gallery
Hysterectomy
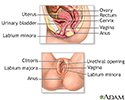
The female reproductive system is a very complex system. And as with any system, occasionally, things go wrong. When treatments and therapies can't fix an issue, sometimes surgery is required. Surgery to remove a woman's uterus or womb, a major component of this system, is called hysterectomy. Let's talk about this procedure.
There are many reasons a woman may need a hysterectomy: cancer of the uterus, usually endometrial cancer; cancer of the cervix; childbirth complications, such as uncontrolled bleeding; other long-term vaginal bleeding problems; long-term pelvic pain. Other reasons include severe endometriosis, including growths outside the uterus; slipping of the uterus into the vagina and perhaps tumors in the uterus, such as uterine fibroids.
During a hysterectomy, your doctor may remove the entire uterus or just part of it. The fallopian tubes, which connect the ovaries to the uterus, and the ovaries themselves may also be removed.
There are several different ways to perform a hysterectomy. It may be done through a surgical cut in either the belly or vagina. It may be done using laparoscopy, using a camera and smaller incisions, or it may be performed using robotic surgery. Your doctor will help you decide which type of procedure is best for you.
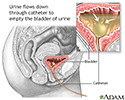
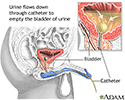
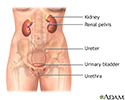
After surgery, you will receive pain medications to relieve discomfort. You may also have a tube, called a catheter, inserted into your bladder for a day or two to pass urine. You will be asked to get up and move around as soon as possible after surgery; this helps prevent blood clots from forming in your legs and speeds up recovery.
How long you stay in the hospital depends on the type of hysterectomy. If you have a robot-assisted hysterectomy, you will likely go home the next day. Most women who have a hysterectomy, however, will stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days, maybe even longer if you have a hysterectomy due to cancer.
Recovery may take anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the type of hysterectomy you have. A hysterectomy will cause menopause if you also have your ovaries removed. Removal of the ovaries can also lead to a decreased sex drive. Your doctor, then, may recommend estrogen replacement therapy. There is some good news. Removing the problematic organs should keep you from having problems in this area again.
Hysterectomy
Review Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Peter J. Chen, MD, FACOG, Associate Professor of OBGYN at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Animations
Illustrations
- 17 week ultrasound
- 30 week ultrasound
- Abdominal organs
- Abdominal quadrants
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abnormal discharge from the...
- Actinic keratosis - close-up
- Actinic keratosis - ear
- Actinic keratosis on the arm
- Actinic keratosis on the fo...
- Actinic keratosis on the scalp
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia ...
- Acute monocytic leukemia - skin
- Adenocarcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma - chest x-ray
- Adrenal gland biopsy
- Adrenal gland hormone secretion
- Adrenal metastases - CT scan
- Adrenal Tumor - CT
- Aging spots
- Anatomical landmarks adult ...
- Antibodies
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic rupture - chest x-ray
- Appendicitis
- Ascites with ovarian cancer...
- Auer rods
- Barium enema
- Barium ingestion
- Basal cell cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma - close-up
- Basal cell carcinoma - close-up
- Basal Cell Carcinoma - face
- Basal cell carcinoma - nose
- Basal cell nevus syndrome
- Basal cell nevus syndrome -...
- Basal cell nevus syndrome - face
- Basal cell nevus syndrome -...
- Basal cell nevus syndrome -...
- Basophil (close-up)
- Before and after hematoma repair
- Benign juvenile melanoma
- Benign tumor of the skin
- Bile pathway
- Biopsy catheter
- Bladder biopsy
- Bladder catheterization - female
- Bladder catheterization - male
- Blood cells
- Blood test
- Bone biopsy
- Bone density scan
- Bone marrow aspiration
- Bone marrow from hip
- Bowen's disease on the hand
- BPH
- Brain
- Brain wave monitor
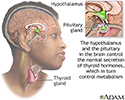
- Brain-thyroid link
- Breast lumps
- Breast pain
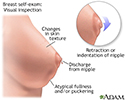
- Breast self-exam
- Breast self-exam
- Breast self-exam
- Bronchial cancer - chest x-ray
- Bronchial cancer - CT scan
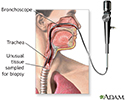
- Bronchoscope
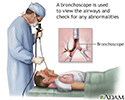
- Bronchoscopy
- Bronchoscopy
- Burns
- Calculating body frame size
- Candida - fluorescent stain
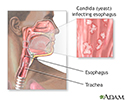
- Candidal esophagitis
- Canker sore (aphthous ulcer)
- Carotid duplex
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carpal biopsy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Causes of breast lumps
- Causes of breast lumps
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cervical biopsy
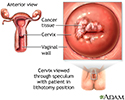
- Cervical cancer
- Cervical cancer
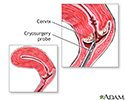
- Cervical cryosurgery
- Cervical cryosurgery
- Cervical neoplasia
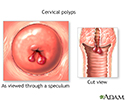
- Cervical polyps
- Changes in face with age
- Changes in lung tissue with age
- Changes in skin with age
- Cheilitis - actinic
- Child thyroid anatomy
- Cholesterol producers
- Chromosomes and DNA
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemi...
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia...
- Cirrhosis of the liver
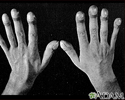
- Clubbing
- Coal worker's lungs - chest...
- Coal workers pneumoconiosis...
- Coal workers pneumoconiosis...
- Coal workers pneumoconiosis...
- Coal workers pneumoconiosis...
- Coccidioidomycosis - chest x-ray
- Cold cone biopsy
- Cold cone removal
- Colon culture
- Colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Colposcopy-directed biopsy
- Congenital nevus on the abdomen
- Cryoglobulinemia of the fingers
- CSF cell count
- CSF protein test
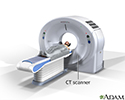
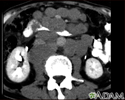
- CT scan
- Cystography
- Cystoscopy
- Diet and disease prevention
- Digestive system
- Digestive system organs
- Donor liver attachment
- Emphysema
- Endocrine glands
- Endometrial biopsy
- Endometrial biopsy
- Endometrial cancer
- Enlarged spleen
- Epithelial cells
- ERCP
- ERCP
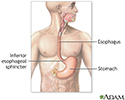
- Esophagus and stomach anatomy
- Ewing sarcoma - x-ray
- Eye
- Facial drooping
- Fat tissue biopsy
- Fatty liver - CT scan
- Fecal occult blood test
- Female breast
- Female breast biopsy
- Female perineal anatomy
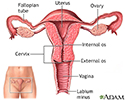
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy
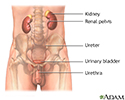
- Female urinary tract
- Fibroadenoma
- Fibrocystic breast change
- Fibroid tumors
- Formed elements of blood
- Gallbladder anatomy
- Gallbladder endoscopy
- Gallium injection
- Gallstones
- Gallstones, cholangiogram
- Gum biopsy
- Hairy cell leukemia - micro...
- Half and half nails
- Hand X-ray
- Head and neck glands
- Headache
- Heart - front view
- Heart - section through the...
- Heartburn prevention
- Hemangioma - angiogram
- Hemangioma - CT scan
- Hemoglobin
- Hemorrhoids
- Hepatocellular cancer - CT scan
- Hepatomegaly
- Hodgkin's disease - liver i...
- Hydrocele
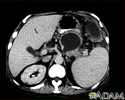
- Hysterectomy
- Ileus - x-ray of bowel dist...
- Ileus - x-ray of distended ...
- Immune system structures
- Incision for lung biopsy
- Incision for pleural tissue...
- Incision for thyroid gland ...
- Intraductal papilloma
- Intravenous pyelogram
- Intussusception - x-ray
- Jaundice
- Jaundiced infant
- Kaposi sarcoma - close-up
- Kaposi sarcoma - lesion on ...
- Kaposi sarcoma - perianal
- Kaposi sarcoma on foot
- Kaposi sarcoma on the back
- Kaposi's sarcoma on the thigh
- Keratoacanthoma
- Keratoacanthoma
- Kidney - blood and urine flow
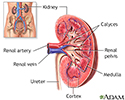
- Kidney anatomy
- Kidney function
- Kidney function tests
- Kidney metastases - CT scan
- Kidney tumor - CT scan
- Kidneys
- Koilonychia
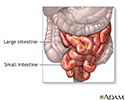
- Large intestine (colon)
- Large intestine anatomy
- Lentigo - solar on the back
- Lentigo - solar with erythe...
- Leucine aminopeptidase urin...
- Lichen planus on the oral mucosa
- Lipoma - arm
- Liver biopsy
- Liver cirrhosis - CT scan
- Liver function tests
- Liver metastases, CT scan
- Liver with disproportional ...
- Lobes of the brain
- Lower digestive anatomy
- Lumpectomy
- Lung biopsy
- Lung cancer - chemotherapy ...
- Lung cancer - frontal chest...
- Lung cancer - lateral chest...
- Lung mass, right lung - CT scan
- Lung mass, right upper lobe...
- Lung mass, right upper lung...
- Lung nodule - front view ch...
- Lung nodule, right lower lu...
- Lung nodule, right middle l...
- Lung tissue biopsy
- Lung with squamous cell can...
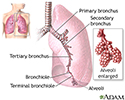
- Lungs
- Lymph node metastases, CT scan
- Lymphangiogram
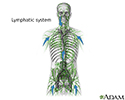
- Lymphatic system
- Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
- Malaria, microscopic view o...
- Malaria, photomicrograph of...
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male reproductive system
- Male urinary system
- Male urinary tract
- Malignancy
- Malignant melanoma
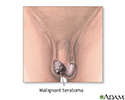
- Malignant teratoma
- Mammary gland
- Mammogram
- Mammography
- Mediastinoscopy
- Megaloblastic anemia - view...
- Melanoma
- Melanoma - neck
- Melanoma of the liver - MRI scan
- MIBG injection
- Mongolian blue spots
- Mouth anatomy
- Mouth sores
- MRI scans
- Multiple basal cell cancer ...
- Muscle biopsy
- Nail infection - candidal
- Nasal biopsy
- Neck lump
- Needle biopsy of the breast
- Nerve biopsy
- Neuroblastoma in the liver ...
- Neurofibromatosis I - enlar...
- Non-small cell carcinoma
- Normal external abdomen
- Normal female breast anatomy
- Normal lung anatomy
- Normal lungs and alveoli
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Onycholysis
- Open biopsy of the breast
- Oral anatomy
- Oral thrush
- Oropharyngeal biopsy
- Oropharynx
- Osteogenic sarcoma - x-ray
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis
- Ovalocytosis
- Ovarian cancer
- Ovarian cancer dangers
- Ovarian cancer metastasis
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian cysts
- Ovarian growth worries
- Pancreas
- Pancreatic cancer, CT scan
- Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
- Pancreatic, cystic adenoma ...
- Pap smear
- Pap smear
- Pap smears and cervical cancer
- Parathyroid biopsy
- Pelvic adhesions
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Peritoneal and ovarian canc...
- Physical activity - prevent...
- Phytochemicals
- Pleural biopsy
- Pleural cavity
- Pleural smear
- Pleural space
- Primary and secondary hypot...
- Primary brain tumor
- Prostate cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Prostate gland
- PSA blood test
- Ptosis - drooping of the eyelid
- Pulmonary mass - side view ...
- Pulmonary nodule - front vi...
- Pulmonary nodule, solitary ...
- Quitting smoking
- Radiation therapy
- Rectal biopsy
- Rectal cancer - x-ray
- Red blood cells - elliptocytosis
- Red blood cells - multiple ...
- Red blood cells - normal
- Red blood cells - sickle an...
- Red blood cells - sickle cells
- Red blood cells - spherocytosis
- Red blood cells, sickle cell
- Red blood cells, target cells
- Red blood cells, tear-drop shape
- Renal biopsy
- Respiratory cilia
- Respiratory system
- Retina
- Salivary gland biopsy
- Sarcoid, stage II - chest x-ray
- Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray
- Scrotal mass
- Secondhand smoke and lung cancer
- Selenium - antioxidant
- Sentinel node biopsy
- Serotonin uptake
- Sigmoid colon cancer - x-ray
- Sinuses
- Skeletal spine
- Skeleton
- Skeleton (posterior view)
- Skin
- Skin cancer - close-up of l...
- Skin cancer - close-up of l...
- Skin cancer - malignant melanoma
- Skin cancer - melanoma supe...
- Skin cancer - raised multi-...
- Skin cancer - squamous cell...
- Skin cancer, basal cell car...
- Skin cancer, basal cell car...
- Skin cancer, basal cell car...
- Skin cancer, basal cell car...
- Skin cancer, close-up of le...
- Skin cancer, melanoma - fla...
- Skin cancer, melanoma - rai...
- Skin cancer, melanoma on th...
- Skin cancer, squamous cell ...
- Skin layers
- Skull of an adult
- Small bowel obstruction - x-ray
- Small cell carcinoma
- Small intestine
- Small intestine biopsy
- Smoking hazards
- Smoking hazards
- Spermatocele
- Spinal tumor
- Spleen and liver metastases...
- Splenomegaly
- Squamous cell cancer
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma - i...
- Stages of cancer
- Sternum - view of the outsi...
- Stomach
- Stomach cancer, x-ray
- Stomach ulcer, x-ray
- Structure of the colon
- Sun protection
- Sunburn
- Sunburn
- Sunburn
- Superficial anterior muscles
- Surface anatomy - normal palm
- Surface anatomy - normal wrist
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin
- Swollen lymph nodes under arm
- Synovial biopsy
- Temperature measurement
- Teratoma - MRI scan
- Testicular anatomy
- Testicular biopsy
- Testicular ultrasound
- The large intestine
- Thermometer temperature
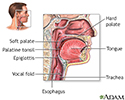
- Throat anatomy
- Thyroid cancer - CT scan
- Thyroid cancer - CT scan
- Thyroid enlargement - scintiscan
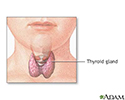
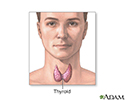
- Thyroid gland
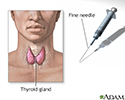
- Thyroid gland biopsy
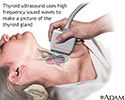
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Tobacco and cancer
- Tobacco and chemicals
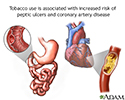
- Tobacco and vascular disease
- Tobacco health risks
- Tongue
- Tongue biopsy
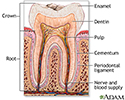
- Tooth anatomy
- Tuberculosis, advanced - ch...
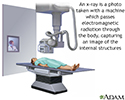
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound comparison
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Upper airway test
- Upper gastrointestinal system
- Ureteral biopsy
- Urine test
- Uterine anatomy
- Uterus
- Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
- Vertebrae
- Viral lesion culture
- Visual acuity test
- Visual field test
- Vitamin B3 source
- Vitamin B6 benefit
- Vitamin C benefit
- Volvulus - x-ray
- Waldenström
- Wart (verruca) with a cutan...
- Warts - flat on the cheek a...
- Warts, multiple - on hands
- White nail syndrome
- Wilms tumor
- X-ray
- Yellow nail syndrome
- Yellow nails
Presentations
- Biliary obstruction - series
- Breast lump removal - series
- Colon cancer - series
- Colostomy - series
- Exchange transfusion - series
- Gastrectomy - series
- Hemorrhoid surgery - series
- Hysterectomy - Series
- Large bowel resection - series
- Mastectomy - series
- Prostatectomy - Series
- Pulmonary lobectomy - series
- Small bowel resection - series
- Spleen removal - series
- Transurethral resection of ...

 Bookmark
Bookmark