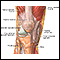
Necrotizing vasculitis
Necrotizing vasculitis is a group of disorders that involve inflammation of the blood vessel walls. The size of the affected blood vessels helps to determine the names of these conditions and how the disorder causes disease.
Causes
Necrotizing vasculitis may be the primary condition such as in people with polyarteritis nodosa or granulomatosis with ANCA associated vasculitis (formerly called Wegener granulomatosis). In other cases, the vasculitis may occur as part of another disorder, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or hepatitis C.
Polyarteritis nodosa
Polyarteritis nodosa is a serious inflammatory blood vessel disease. The small and medium-sized arteries become swollen and damaged.
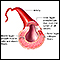
Granulomatosis with ANCA associated vas...
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a rare disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. This leads to damage in major organs of the body. ...
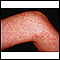
The cause of the inflammation is unknown. It is likely related to autoimmune factors. The wall of the blood vessel may scar and thicken or die (become necrotic). The blood vessel may close, interrupting blood flow to the tissues it supplies. The lack of blood flow will cause the tissues to die. Sometimes the blood vessel may break and bleed (rupture).
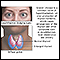
Autoimmune
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune di...
Necrotic
Necrosis is the death of body tissue. It occurs when too little blood flows to the tissue. This can be from injury, infection, radiation, or chemic...

Necrotizing vasculitis may affect blood vessels in any part of the body. Therefore, it can cause problems in the skin, brain, lungs, intestines, kidney, brain, joints or any other organ.
Symptoms
Fever, chills, fatigue, arthritis, or weight loss may be the only symptoms at first. However, symptoms may be in almost any part of the body.
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...

Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.

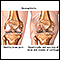
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
Skin:
- Red or purple colored bumps on the legs, hands or other parts of the body
- Bluish color to the fingers and toes
- Signs of tissue death due to lack of oxygen such as pain, redness, darkening of skin tone, and ulcers that do not heal
Muscles and joints:
- Joint pain
- Leg pain
- Muscle weakness
Brain and nervous system:
- Pain, numbness, tingling in an arm, leg, or other body area
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness of an arm, leg, or other body area
- Pupils that are different sizes
- Eyelid drooping
- Swallowing difficulty
Swallowing difficulty
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Speech impairment
Speech impairment
Speech and language impairment may be any of several problems that make it difficult to communicate.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Movement difficulty
Lungs and respiratory tract:
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sinus congestion and pain
- Coughing up blood or bleeding from the nose
Other symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
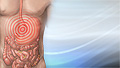 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood in the urine or stools
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
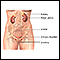 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleStools
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the ...
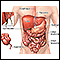 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hoarseness or changing voice
- Chest pain from damage of the arteries that supply the heart (coronary arteries)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a complete physical exam. A nervous system (neurological) exam may show signs of nerve damage.
Tests that may be done include:
- Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
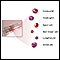 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Comprehensive metabolic panel
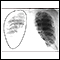
- Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - C-reactive protein test
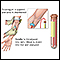
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is commonly called a "sed rate. "It is a test that indirectly measures the level of certain protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatitis blood test
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood test for antibodies against neutrophils (ANCA antibodies) or nuclear antigens (ANA)
- Blood test for cryoglobulins
- Blood test for complement levels
Complement
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of ne...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
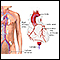
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Imaging studies such as angiogram, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Angiogram
An arteriogram is an imaging test that uses x-rays and a special dye to see inside the arteries. It can be used to view arteries in the heart, brain...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Biopsy of the skin, muscle, organ tissue, or nerve
Biopsy
A muscle biopsy is the removal of a small piece of muscle tissue for examination.
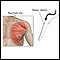 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNerve
A nerve biopsy is the removal of a small piece of a nerve for examination.
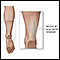 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Corticosteroids are given in most cases. The dose will depend on how bad the condition is.
Other medicines that suppress the immune system may reduce inflammation of the blood vessels. These include azathioprine, methotrexate, and mycophenolate. These medicines are often used along with corticosteroids. This combination makes it possible to control the disease with a lower dose of corticosteroids.
For severe disease, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) has been used for many years. However, rituximab (Rituxan) is equally effective and is less toxic.
Recently, tocilizumab (Actemra) was shown to be effective for giant cell arteritis so the dose of corticosteroids could be reduced.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Necrotizing vasculitis can be serious and life-threatening disease. The outcome depends on the location of the vasculitis and the severity of tissue damage. Complications may occur from the disease and from the medicines. Most forms of necrotizing vasculitis require long-term follow-up and treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Permanent damage to the structure or function of the affected area
- Secondary infections of necrotic tissues
Secondary infections
A secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after treatment for another infection. It may be caused by the first treatment or by cha...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Side effects from medicines used for treatment
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of necrotizing vasculitis.
Emergency symptoms include:
- Problems in more than one part of the body such as stroke, arthritis, severe skin rash, abdominal pain or coughing up blood
- Changes in pupil size
- Loss of function of an arm, leg, or other body part
- Speech problems
- Swallowing difficulty
- Weakness
- Severe abdominal pain
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent this disorder.
Reviewed By
Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Chung SA, Monach PA. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 90.
Dinulos JGH. Hypersensitivity syndromes and vasculitis. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Free M, Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Jain K. Renal and systemic vasculitis. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 26.
Rhee RL, Merkel PA. Classification and epidemiology of systemic vasculitis. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 88.
Stone JH. The systemic vasculitides. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 249.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.