Fungal arthritis

Definition
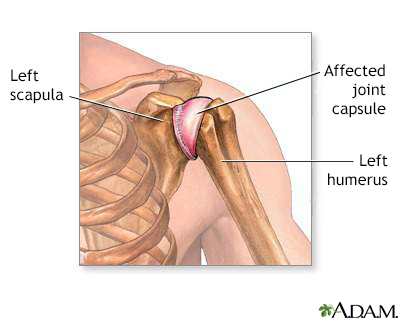
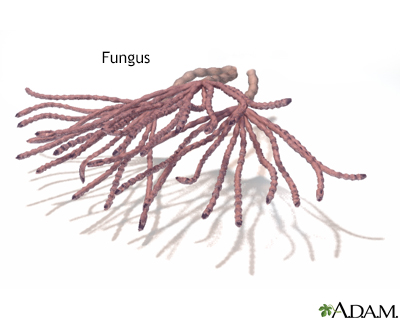
Fungal arthritis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of a joint by a fungal infection. It is also called mycotic arthritis.
Causes
Fungal arthritis is a rare condition. It can be caused by any of the invasive types of fungi. The infection can result from an infection in another organ, such as the lungs and travel to a joint through the bloodstream. A joint can also become infected during a surgery. People with weakened immune systems who travel or live in areas where the fungi are common, are more susceptible to most causes of fungal arthritis.
Conditions that can cause fungal arthritis include:
Symptoms
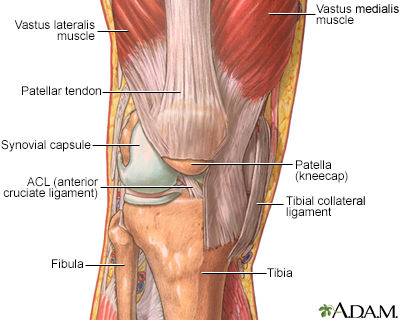
The fungus can affect bone or joint tissue. One or more joints can be affected, most often the large, weight-bearing joints, such as the knees.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Removal of joint fluid to look for fungus under a microscope
- Culture of joint fluid to look for fungus
- Joint x-ray that may show joint changes
- Positive antibody test (serology) for fungal disease
- Synovial biopsy showing fungus
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection using antifungal medicines. Commonly used antifungal medicines are amphotericin B or medicines in the azole family (fluconazole, ketoconazole, or itraconazole).
Chronic or advanced bone or joint infection may require surgery (debridement) to remove the infected tissue.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on the underlying cause of the infection and your overall health. A weakened immune system, cancer, and certain medicines can affect the outcome.
Possible Complications
Joint damage may occur and the risk of damage is higher if the infection is not treated right away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if you have any symptoms of fungal arthritis.
Prevention
Thorough treatment of fungal infections elsewhere in the body may help prevent fungal arthritis.
References
Ohl CA. Infectious arthritis of native joints. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 103.
Ruderman EM, Flaherty JP. Fungal infections of bones and joints. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein and Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 119.
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.