Meningitis
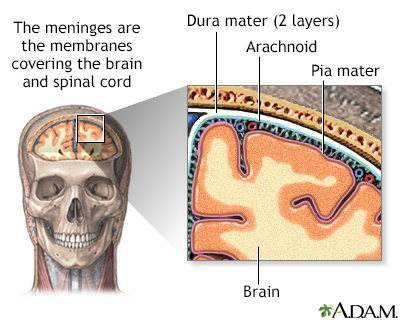
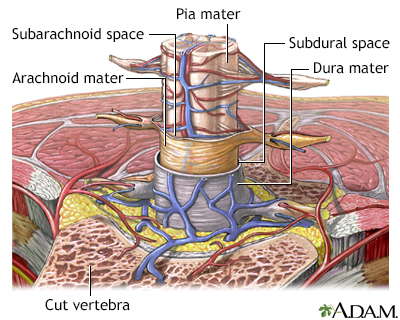
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
Causes
The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections. These infections usually get better without treatment. Bacterial meningitis infections, however, are very serious. They may result in death or brain damage, even if treated. A lumbar puncture (or spinal tap) is required to determine the specific cause.
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Meningitis may also be caused by:
- Chemical irritation
- Medicine allergies
- Fungi
- Parasites
- Tumors
Many types of viruses can cause meningitis:
- Enteroviruses: These are viruses that also can cause intestinal illness.
- Herpes viruses: These are the same viruses that can cause cold sores and genital herpes. However, people with cold sores or genital herpes do not have a higher chance of developing herpes meningitis.
Genital herpes
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This article focuses on HSV type 2 infection....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - HIV: This virus can cause meningitis during the early stages of HIV infection.
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mumps virus: This virus causes a contagious disease that leads to painful swelling of the salivary glands. Meningitis is a complication of a mumps infection.
Mumps virus
Mumps is a contagious disease that leads to painful swelling of the salivary glands. The salivary glands produce saliva, a liquid that moistens food...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - West Nile virus: This virus is spread by mosquito bites and is an important cause of viral meningitis in most of the United States.
West Nile virus
West Nile virus causes a viral disease and is spread by mosquitoes. The condition ranges from mild to severe.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Enteroviral meningitis occurs more often than bacterial meningitis and is milder. It usually occurs in the late summer and early fall. It most often affects children and adults under age 30. Symptoms may include:
- Headache
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Slight fever
- Upset stomach and diarrhea
- Fatigue
Bacterial meningitis is an emergency. You will need immediate treatment in a hospital. Symptoms usually come on quickly, and may include:
- Fever and chills
- Mental status changes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease:
- Agitation
Agitation
Agitation is an unpleasant state of extreme arousal. An agitated person may feel stirred up, excited, tense, confused, or irritable.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Bulging fontanelles in babies
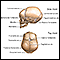
Bulging fontanelles
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased alertness
- Poor feeding or irritability in children
- Rapid breathing
- Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backward (opisthotonos)
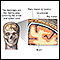
Opisthotonos
Opisthotonos is a condition in which a person holds their body in an abnormal position. The person is usually rigid and arches their back, with thei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You cannot tell if you have bacterial or viral meningitis by how you feel. Your health care provider must find out the cause. Go to a hospital emergency department right away if you think you have symptoms of meningitis.
Exams and Tests
Your provider will examine you. This may show:
- Fast heart rate
- Fever
- Mental status changes
- Stiff neck
If your provider thinks you have meningitis, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) should be done to remove a sample of spinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF) for testing.
Other tests that may be done include:
- Blood culture
- Chest x-ray
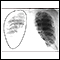
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of the head
Treatment
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial meningitis. Antibiotics do not treat viral meningitis. However, antiviral medicine may be given to those with herpes meningitis.
Other treatments will include:
- Fluids through a vein (intravenous)
- Medicines to treat symptoms, such as brain swelling, shock, and seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Outlook (Prognosis)
Early diagnosis and treatment of bacterial meningitis is essential to prevent permanent neurological damage. Viral meningitis is usually not serious, and symptoms should disappear within 2 weeks with no lasting complications.
Possible Complications
Without prompt treatment, meningitis may result in the following:
- Brain or neurologic damage
- Buildup of fluid between the skull and brain (subdural effusion)
- Hearing loss
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
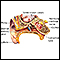 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling (hydrocephalus)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you think that you or your child has symptoms of meningitis, get emergency medical help immediately. Early treatment is key to a good outcome.
Prevention
Certain vaccines can help prevent some types of bacterial meningitis:
- Haemophilus vaccine (HiB vaccine) is given to children.
HiB vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Hib (Haemophilus Influenzae Type b) Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pneumococcal vaccine is given to children and adults.
Children
Content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-vis/pneumococcal-conjugate. html...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAdults
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): CDC review information for P...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Meningococcal vaccine is given to children and adults; some communities hold vaccination campaigns after an outbreak of meningococcal meningitis.
Children and adults
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Meningococcal ACWY Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-vi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Household members and others in close contact with people who have meningococcal meningitis should receive antibiotics to prevent becoming infected.
Reviewed By
Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Hasbun R, Van de Beek D, Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR. Acute meningitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 87.
Nath A. Meningitis: bacterial, viral, and other. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 381.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.