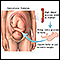
Tricuspid atresia
Tricuspid atresia is a type of heart disease that is present at birth (congenital heart disease), in which the tricuspid heart valve is missing or abnormally developed. The defect blocks blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Other heart or vessel defects are usually present at the same time.
Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a problem with the heart's structure and function that is present at birth.
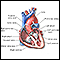
Causes
Tricuspid atresia is an uncommon form of congenital heart disease. Infants born with tricuspid atresia often also have atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect.
Atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a heart defect that is present at birth (congenital). As a baby develops in the womb, a wall (septum) forms that divide...
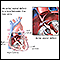
Ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect is a hole in the wall that separates the right and left ventricles of the heart. Ventricular septal defect is one of the...

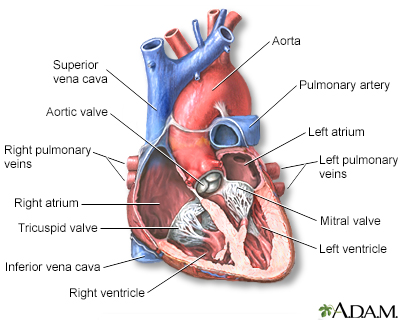
Normally, blood flows from the body into the right atrium, then through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle and on to the lungs. If the tricuspid valve does not open, the blood cannot flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Because of the problem with the tricuspid valve, blood ultimately cannot enter the lungs. This is where it must go to pick up oxygen (becomes oxygenated).
Instead, the blood passes through a hole between the right and left atrium. In the left atrium, it mixes with oxygen-rich blood returning from the lungs. This mix of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood is then pumped out into the body from the left ventricle. This causes the oxygen level in the blood to be lower than normal.
In people with tricuspid atresia, the lungs receive blood either through a hole between the right and left atria (described above), or through maintenance of a fetal blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus. The ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary artery (artery to the lungs) to the aorta (main artery to the body). It is present when a baby is born, but normally closes by itself shortly after birth.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
-
Bluish color to the skin (cyanosis) due to low oxygen level in the blood
Bluish color to the skin
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fast breathing
- Fatigue
- Poor growth
- Shortness of breath
Exams and Tests
This condition may be discovered during routine prenatal ultrasound imaging or when the baby is examined after birth. Bluish skin is present at birth. A heart murmur is often present at birth and may increase in loudness over several months.
Prenatal ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of how a baby is developing in the womb (uterus). It is also use...
Tests may include the following:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves passing a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the right or left side of the heart. The catheter is most often insert...
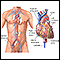 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the heart
MRI of the heart
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the heart
CT scan of the heart
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create detailed pictures of the heart and its blood vessels. Th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Once the diagnosis is made, the baby will often be admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). A medicine called prostaglandin E1 may be used to keep the ductus arteriosis open (patent) so that blood can circulate to the lungs.
Generally, patients with this condition require surgery. If the heart is unable to pump enough blood out to the lungs and rest of the body, the first surgery most often takes place within the first few days of life. In this procedure, an artificial shunt is inserted to keep blood flowing to the lungs. In some cases, this first surgery is not needed.
Afterward, the baby goes home in most cases. The child will need to take one or more daily medicines and be closely followed by a pediatric cardiologist (heart specialist). This doctor will decide when the second stage of surgery should be done.
The next stage of surgery is called the Glenn shunt or hemi-Fontan procedure. This procedure connects half of the veins carrying oxygen-poor blood from the upper half of the body directly to the pulmonary artery. The surgery is most often done when the child is between 4 to 6 months old.
During stage I and II, the child may still look blue (cyanotic).
Stage III, the final step, is called the Fontan procedure. The rest of the veins carrying oxygen-poor blood from the body are connected directly to the pulmonary artery leading to the lungs. The left ventricle now only has to pump to the body, not the lungs. This surgery is usually performed when the child is 18 months to 3 years old. After this final step, the baby's skin is no longer blue.
Outlook (Prognosis)
In most cases, surgery will improve the condition.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Irregular, fast heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic diarrhea (from a disease called protein-losing enteropathy)
Protein-losing enteropathy
Protein-losing enteropathy is an abnormal loss of protein from the digestive tract. It can also refer to the inability of the digestive tract to abs...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid in the abdomen (ascites) and in the lungs (pleural effusion)
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.
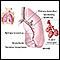 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blockage of the artificial shunt
- Strokes and other nervous system complications
- Sudden death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your child's health care provider right away if your child has:
- New changes in breathing patterns
- Problems eating
- Skin that is turning blue
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent tricuspid atresia.
Women who plan to become pregnant should be immunized against rubella if they are not already immune. Rubella infection in a pregnant woman can cause congenital heart disease.
Rubella
Rubella, also known as the German measles, is an infection in which there is a rash on the skin. Congenital rubella is when a pregnant woman with rub...
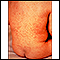
Women who are pregnant should get good prenatal care:
- Avoid alcohol and illegal drugs during pregnancy.
- Tell your provider that you are pregnant before taking any new medicines.
- Have a blood test early in your pregnancy to see if you are immune to rubella. If you are not immune, avoid any possible exposure to rubella and get vaccinated right after delivery.
- Pregnant women who have diabetes should try to get good control over their blood sugar level.
Good control over their blood sugar lev...
Gestational diabetes is diabetes, defined by high blood sugar (glucose), that starts during pregnancy. If you've been diagnosed with gestational dia...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some inherited factors may play a role in congenital heart disease. Many family members may be affected. If you are planning to get pregnant, talk to your provider about screening for genetic diseases.
Reviewed By
Thomas S. Metkus MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Bernstein D. Cyanotic congenital heart disease: evaluation of the critically ill neonate with cyanosis and respiratory distress. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 478.
Valente AM, Dorfman AL, Babu-Narayan SV, Kreiger EV. Congenital heart disease in the adolescent and adult. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 82.
Well A, Fraser CD. Congenital heart disease. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 59.
Disclaimer


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.