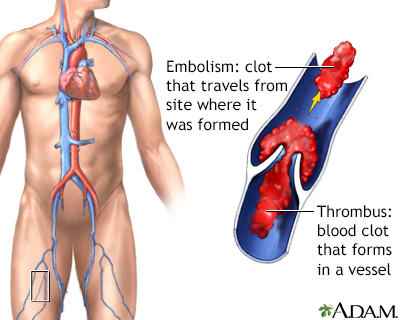
Blood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid.
- A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is called a thrombus. A thrombus may also form in your heart.
- A thrombus that breaks loose and travels from one location in the body to another is called an embolus.
A thrombus or embolus can partly or completely block the flow of blood in a blood vessel.
- A blockage in an artery may prevent oxygen from reaching the tissues in that area. This is called ischemia. If ischemia is not treated promptly, it can lead to tissue damage or death.
- A blockage in the vein will often cause fluid buildup and swelling in the area where blood is drained by that vein.
Causes
Situations in which a blood clot is more likely to form in veins include:
- Being on long-term bed rest
- Sitting for long periods, such as in a plane or car
- During and after pregnancy
- Taking birth control pills or estrogen hormones (especially in women who smoke)
- Long-term use of an intravenous catheter
- After surgery
Blood clots are also more likely to form after an injury. People with cancer, obesity, and liver or kidney disease are also prone to blood clots.
Obesity
Obesity means weighing more than what is healthy for a given height. Obesity is a serious, chronic disease. It can lead to other health problems, i...
Smoking also increases the risk of forming blood clots.
Conditions that are passed down through families (inherited) may make you more likely to form abnormal blood clots. Inherited conditions that affect clotting are:
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Prothrombin G20210A mutation
Other rare conditions, such as protein C, protein S, and antithrombin III deficiencies.
A blood clot may block an artery or vein in an organ, affecting the:
- Heart (angina or a heart attack)
Angina
Angina is a type of chest discomfort or pain due to poor blood flow through the blood vessels (coronary arteries) of the heart muscle (myocardium). ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
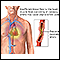
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intestines (mesenteric ischemia or mesenteric venous thrombosis)
- Kidneys (renal vein thrombosis)
- Leg or arm arteries
Leg or arm arteries
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition of the blood vessels that supply the legs and feet. It occurs due to narrowing of the arteries in the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
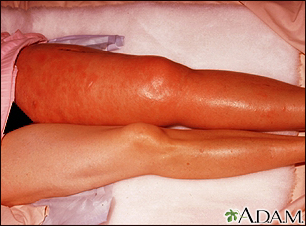
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein deep inside a part of the body. DVT mainly affects the large...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Neck or brain (stroke)
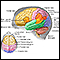
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Anderson JA, Weitz JI. Hypercoagulable states. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 138.
Cross SS. Ischaemia, infarction and shock . In: Cross SS, ed. Underwood's Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 7.
Schafer AI. Approach to the patient with bleeding or thrombosis: hypercoagulable states. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 157.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.