Sheehan syndrome

Endocrine glands
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
Sheehan syndrome is a condition that can occur in a woman who bleeds severely during childbirth. Sheehan syndrome is a type of hypopituitarism.
Causes
Severe bleeding during childbirth can cause tissue in the pituitary gland to die. This prevents the pituitary gland from functioning normally.
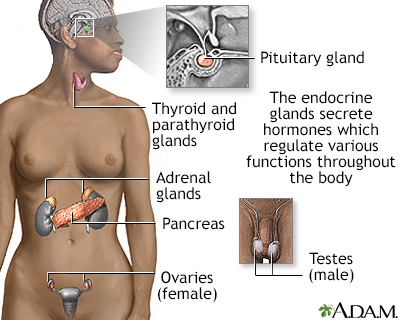
The pituitary gland is at the base of the brain. It makes hormones that stimulate growth, production of breast milk, reproductive functions, the thyroid, and the adrenal glands. A lack of these hormones can lead to a variety of symptoms. Conditions that increase the risk of bleeding during childbirth and Sheehan syndrome include multiple pregnancy (twins or triplets) and problems with the placenta. The placenta is the organ that develops during pregnancy to feed the fetus.
The condition is rare today due to advances in obstetric care.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Sheehan syndrome may include:
- Inability to breastfeed (breast milk never "comes in")
- Fatigue
- Lack of menstrual bleeding
- Loss of pubic and armpit (axillary) hair
- Low blood pressure
Note: Other than not being able to breastfeed, symptoms may not develop for several years after the delivery.
Exams and Tests
Tests done may include:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels
- MRI of the head to check for other pituitary problems, such as a tumor
Treatment
Treatment involves estrogen and progesterone hormone replacement therapy. These hormones must be taken at least until the normal age of menopause. Thyroid and adrenal hormones must also be taken. These will be needed for the rest of your life.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook with early diagnosis and treatment is excellent.
Possible Complications
This condition can be life threatening if not treated.
Prevention
Severe loss of blood during childbirth can often be prevented by proper medical care. Otherwise, Sheehan syndrome is not preventable.
References
Erin K, Aliya K. Other endocrine disorders of pregnancy. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 62.
Huang W, Molitch ME. Pituitary and adrenal disorders in pregnancy. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 48.
Kaiser U, Ho KKY. Pituitary physiology and diagnostic evaluation. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 6.
Review Date: 10/15/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.