Muscle disorder

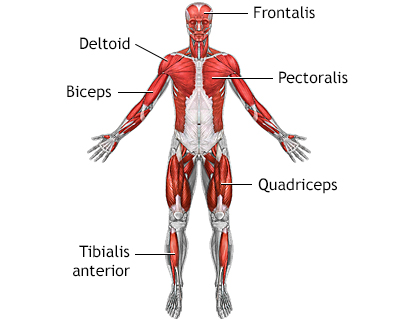
Superficial anterior muscles
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
A muscle disorder causes patterns of weakness, loss of muscle tissue, electromyogram (EMG) findings, or biopsy results that suggest a muscle problem. The muscle disorder can be inherited, such as muscular dystrophy, or acquired, such as alcoholic or steroid myopathy.
The medical name for muscle disorder is myopathy.
Symptoms
The main symptom is weakness.
Other symptoms include cramps and stiffness.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will take your medical history and perform a neurological exam. Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood and urine tests
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS)
- Muscle biopsy
- Genetic tests to look for conditions that run in families. This can be tested with blood work or sometimes saliva testing.
A muscle biopsy examines a tissue sample under a microscope to confirm disease. Sometimes, a blood or saliva test to check for a genetic disorder is all that is needed based on someone's symptoms and family history.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause. It usually includes:
- Bracing
- Medicines (such as corticosteroids in some cases)
- Enzyme replacement therapy
- Gene replacement therapy
- Physical, respiratory, and occupational therapies
- Preventing the condition from getting worse by treating the underlying condition causing the muscle weakness
- Surgery (sometimes)
Your health care provider can tell you more about your condition and treatment options.
References
Borg K, Ensrud E. Myopathies. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD Jr, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Musculoskeletal Disorders, Pain, and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 136.
Doughty CT, Amato AA. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 109.
Selcen D. Muscle diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney K, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 389.
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.