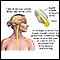
Myelin
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty substances.
This myelin sheath allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells. If myelin is damaged, these impulses slow down. This can cause diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Calabresi PA. Multiple sclerosis and demyelinating conditions. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 380.
Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary. Myelin. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company; 2021. www.tabers.com/tabersonline/view/Tabers-Dictionary/767168/0/myelin?q=myelin. Accessed April 3, 2025.
Disclaimer


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.