Thirst - excessive
Excessive thirst is an abnormal feeling of always needing to drink fluids.
Considerations
Drinking lots of water is healthy in most cases. The urge to drink too much may be the result of a physical or emotional disease. Excessive thirst may be a symptom of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), which may be due to diabetes that is not controlled.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
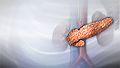
Excessive thirst is a common symptom. It is often the reaction to fluid loss during exercise or to eating salty foods.
Causes
Causes may include:
- A recent salty or spicy meal
- Bleeding enough to cause a large decrease in blood volume
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. DI is not the same as diabetes me...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines such as anticholinergics, demeclocycline, diuretics, phenothiazines
- Loss of body fluids from the bloodstream into the tissues due to conditions such as severe infections (sepsis) or burns, or heart, liver, or kidney failure
- Psychogenic polydipsia (a mental disorder)
Home Care
Because thirst is the body's signal to replace water loss, it is most often appropriate to drink liquids until the thirst sensation is gone.
For thirst caused by diabetes, follow the prescribed treatment to properly control your blood sugar level.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- Excessive thirst is ongoing and unexplained.
- Thirst is accompanied by other unexplained symptoms, such as blurry vision or fatigue.
- You are passing more than 5 quarts (4.75 liters) of urine per day.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will take your medical history and perform a physical exam.
The provider may ask you questions such as:
- How long have you been aware of having increased thirst? Did it develop suddenly or slowly?
- Does your thirst stay the same all day?
- Did you change your diet? Are you eating more salty or spicy foods?
- Have you noticed an increased appetite?
- Have you lost weight or gained weight without trying?
Lost weight
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleGained weight
Unintentional weight gain is when you gain weight without trying to do so and you are not eating or drinking more.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Has your activity level increased?
- What other symptoms are happening at the same time?
- Have you recently suffered a burn or other injury?
- Are you urinating more or less frequently than usual? Are you producing more or less urine than usual? Have you noticed any bleeding?
- Are you sweating more than usual?
- Is there any swelling in your body?
- Do you have a fever?
Tests that may be ordered include the following:
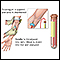
- Blood glucose level
Blood glucose level
A blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CBC and white blood cell differential
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum calcium
- Serum osmolality
- Serum sodium
- Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine osmolality
Your provider will recommend treatment if needed based on your exam and tests. For example, if tests show you have diabetes, you will need to get treated.
A very strong, constant urge to drink may be the sign of a psychological problem. You may need a psychological evaluation if the provider suspects this is a cause. Your fluid intake and output will be closely watched.
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Al-Awqati Q, Radhakrishnan J. Disorders of sodium and water. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 102.
Guber HA, Oprea M, Russell YX. Evaluation of endocrine function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
Verbalis JG. Disorders of water balance. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.




