Satiety - early

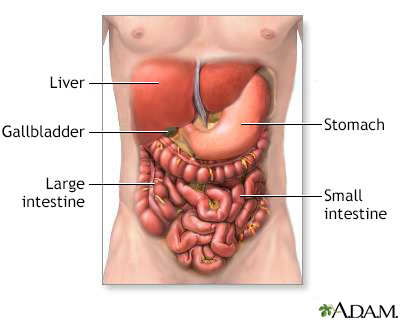
Digestive system organs
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
Satiety is the satisfied feeling of being full after eating. Early satiety is feeling full sooner than normal or after eating less than usual.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Gastric outlet obstruction
- Heartburn
- Nervous system problem that causes delayed stomach emptying
- Stomach or abdominal tumor
- Stomach (peptic) ulcer
Home Care
Follow your health care provider's advice.
- A liquid diet may be helpful.
- You may need to keep a detailed diet log. This is a place where you write down what you eat, how much, and when.
- You may be more comfortable if you eat small, frequent meals rather than big meals.
- A diet high in fat or high in fiber may worsen the feeling.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- The feeling lasts for days to weeks and does not get better.
- You lose weight without trying.
- You have dark stools.
- You have nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, or bloating.
- You have fever and chills.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and ask questions such as:
- When did this symptom begin?
- How long does each episode last?
- What foods, if any, make the symptoms worse?
- What other symptoms do you have (for example, vomiting, excessive gas, abdominal pain, or weight loss)?
Tests that may be performed include:
- Complete blood count and blood differential to check for anemia
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- Stool tests for bleeding
- X-ray studies of the stomach, esophagus, and small intestine (abdominal x-ray and an upper GI and small bowel series)
- Stomach-emptying studies
References
Koch KL. Gastric neuromuscular function and neuromuscular disorders. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 50.
Szabo C, Tantawy H. Diseases of the gastrointestinal system. In: Hines RL, Jones SB, eds. Stoelting's Anesthesia and Co-Existing Disease. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 17.
Review Date: 8/7/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.