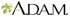Scales

Definition
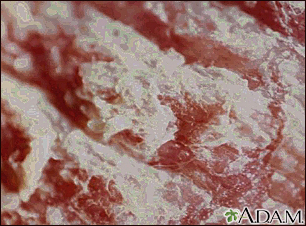
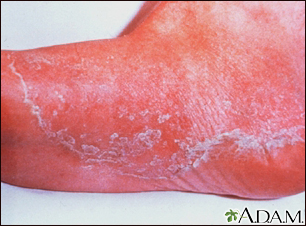
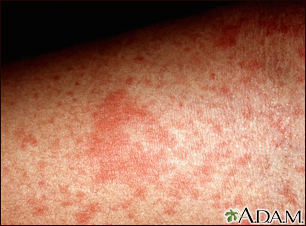
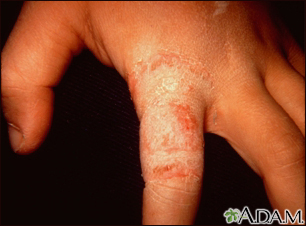
Scales are a visible peeling or flaking of outer skin layers. These layers are called the stratum corneum.
Causes
Scales may be caused by dry skin, certain inflammatory skin conditions, or infections.
Examples of disorders that can cause scales include:
- Eczema
- Fungal infections such as ringworm or tinea versicolor
- Psoriasis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Pityriasis rosea
- Discoid lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disorder
- Genetic skin disorders called ichthyoses
Home Care
If your health care provider diagnoses you with dry skin, you'll likely be recommended the following self-care measures:
- Moisturize your skin with an ointment, cream, or lotion 2 to 3 times a day, or as often as needed.
- Moisturizers help lock in moisture, so they work best on damp skin. After you bathe, pat your skin dry then apply your moisturizer.
- Bathe only once a day. Take short, warm baths or showers. Limit your time to 5 to 10 minutes. Avoid taking hot baths or showers.
- Instead of regular soap, try using gentle skin cleansers or soap with added moisturizers.
- Avoid scrubbing your skin.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Try over-the-counter cortisone creams or lotions if your skin is inflamed.
If your provider diagnoses you with a skin disorder, such as an inflammatory or fungal disease, follow instructions on home care. This may include using a medicine on your skin. You may also need to take a medicine by mouth.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your skin symptoms continue and self-care measures aren't helping.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam to look closely at your skin. You may be asked questions such as when the scaling began, what other symptoms you have, and any self-care you've done at home.
You may need blood tests to check for other conditions.
Treatment depends on the cause of your skin problem. You may need to apply medicine to the skin or take medicine by mouth.
References
James WD. Cutaneous signs and diagnosis. In: James WD, ed. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 2.
Marks JG, Miller JJ, Hollins LC. Scaling papules, plaques, and patches. In: Marks JG, Miller JJ, Hollins LC, eds. Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 9.
Review Date: 6/3/2025
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.