Nikolsky sign

Nikolsky sign
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
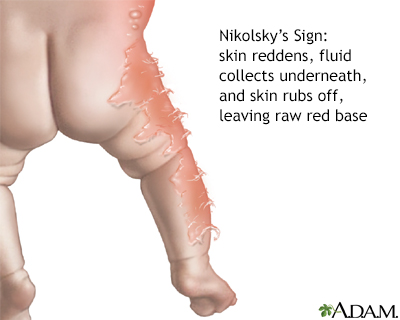
Nikolsky sign is a skin finding in which the top layers of the skin slip away from the lower layers when rubbed.
Considerations
The sign is more common in newborn babies and in young children under 5 years of age. It often begins in the mouth and on neck, shoulder, arm pit, and genital area. A child may be lethargic, irritable, and feverish. They may develop red painful blisters on the skin, which break easily.
Adults with disturbed kidney functions or with a weak immune system may have this sign. Your health care provider may use a pencil eraser or finger to test for Nikolsky sign. The skin is pulled to the side with a shearing pressure on the surface, or by rotating the eraser back and forth.
If the test result is positive, the very thin top layer of skin will shear off, leaving skin pink and moist, and usually very tender.
A positive result is usually a sign of a blistering skin condition. People with a positive sign have loose skin that slips free from the underlying layers when rubbed.
Causes
The Nikolsky sign can be often found in people with:
- Autoimmune blistering conditions such as pemphigus vulgaris
- Bacterial infections such as scalded skin syndrome
- Drug reactions such as erythema multiforme
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child develops painful loosening, redness, and blistering of the skin, which you do not know the cause of (for example, a skin burn).
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The conditions associated with Nikolsky sign can be serious. Some people need to be admitted to the hospital. You will be asked about your medical history and given a physical examination.
Treatment will depend on the cause of the condition.
You may be given:
- Fluid and antibiotics through a vein (intravenously)
- Petroleum jelly to decrease pain
- Local wound care
Healing of the skin blisters occurs in about 1 to 2 weeks with no scarring.
References
Fitzpatrick JE, High WA, Kyle WL. Blisters and vesicles. In: Fitzpatrick JE, High WA, Kyle WL, eds. Urgent Care Dermatology: Symptom-Based Diagnosis. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 11.
Grayson W, Calonje E. Infectious diseases of the skin. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, Billings SD, eds. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 18.
Levin LE, Garzon MC, Lauren CT, Morel KD. Dermatology. In: Polin RA, Ditmar MF, eds. Pediatric Secrets. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 4.
Marco CA. Dermatologic presentations. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 107.
Review Date: 2/15/2024
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.