Coloboma of the iris

Definition
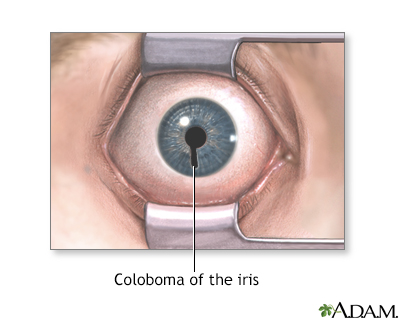
Coloboma of the iris is a hole or defect of the iris of the eye. Most colobomas are present since birth (congenital).
Considerations
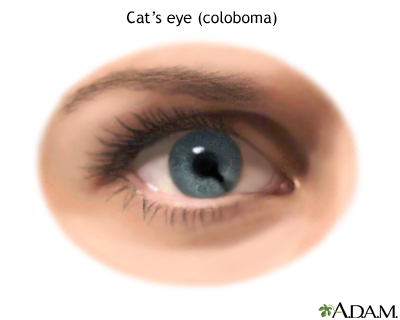
Coloboma of the iris can look like a second pupil or a black notch at the edge of the pupil. This gives the pupil an irregular shape. It can also appear as a split in the iris from the pupil to the edge of the iris.
A small coloboma (especially if it is not attached to the pupil) may allow a second image to focus on the back of the eye. This may cause:
- Blurred vision
- Decreased visual acuity
- Double vision
- Ghost image
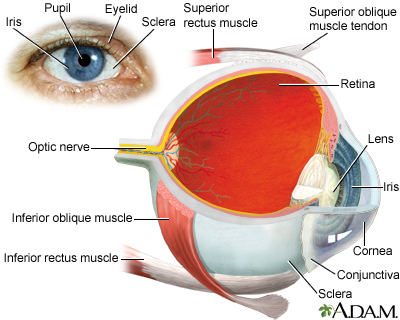
If it is congenital, the defect may include the retina, choroid, or optic nerve.
Most colobomas are diagnosed at birth or shortly afterward.
Causes
Most cases of coloboma have no known cause and are not related to other abnormalities. Some are due to a specific genetic defect. A small number of people with coloboma have other inherited developmental problems.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You notice that your child has what appears to be a hole in the iris or an unusual-shaped pupil.
- Your child's vision becomes blurred or decreased.
In addition to your child, you may also need to see an eye specialist (ophthalmologist).
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and do an exam.
Since the problem is most often diagnosed in infants, knowing about the family history is very important.
The provider will do a detailed eye exam that includes looking into the back of the eye while the eye is dilated. An MRI of the brain, eyes, and connecting nerves may be done if other problems are suspected.
References
Brodsky MC, Houghton O. Congenital optic disc anomalies. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 9.5.
Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA. Congenital and developmental anomalies of the optic nerve. In: Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA, eds. The Retinal Atlas. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 15.
National Eye Institute (NIH) website. Coloboma. www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/coloboma. Updated November 15, 2023. Accessed December 6, 2023.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Abnormalities of pupil and iris. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 640.
Porter D. American Academy of Ophthalmology website. What is a coloboma? www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-is-coloboma. Accessed December 6, 2023.
Selzer EB, Blain D, Hufnagel RB, Lupo PJ, Mitchell LE, Brooks BP. Review of evidence for environmental causes of uveal coloboma. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022;67(4):1031-1047. PMID: 34979194 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34979194/.
Review Date: 11/8/2023
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.