Intercostal retractions
Intercostal retractions occur when the muscles between the ribs pull inward. The movement is most often a sign that the person has a breathing problem.
Intercostal retractions are a medical emergency.
Considerations
The wall of your chest is flexible. This helps you breathe normally. Stiff tissue called cartilage attaches your ribs to the breast bone (sternum).
The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs. During breathing, these muscles normally tighten and pull the rib cage up. Your chest expands and the lungs fill with air.
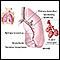
Intercostal retractions are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest. This can happen if the upper airway (trachea) or small airways of the lungs (bronchioles) become partially blocked. As a result, the intercostal muscles are sucked inward, between the ribs, when you breathe. This is a sign of a partially or completely blocked airway. Any health problem that causes a blockage in the airway will cause intercostal retractions.
Blocked airway
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
Causes
Intercostal retractions may be caused by:
- A severe, whole-body allergic reaction called anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening type of allergic reaction.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Asthma
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and become narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling and mucus buildup in the smallest air passages in the lungs (bronchiolitis)
- Problem breathing and a barking cough (croup)
- Inflammation of the tissue (epiglottis) that covers the windpipe
- Foreign body in the windpipe
- Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A lung problem in newborns called respiratory distress syndrome
- Collection of pus in the tissues in the back of the throat (retropharyngeal abscess)
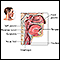
Retropharyngeal abscess
Retropharyngeal abscess is a collection of pus in the tissues in the back of the throat. It can be a life-threatening medical condition.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical help right away if intercostal retractions occur. This can be a sign of a blocked airway, which can quickly become life threatening.
Also seek medical care if the skin, lips, or nailbeds turn blue (cyanosis), or if the person becomes confused, drowsy, or is hard to wake up.
Cyanosis
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.

What to Expect at Your Office Visit
In an emergency, your health care team will first take steps to help you breathe. You may receive oxygen, medicines to reduce swelling, and other treatments.
When you can breathe better, your health care provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms, such as:
- When did the problem start?
- Is it getting better, worse, or staying the same?
- Does it occur all the time?
- Did you notice anything significant that might have caused an airway obstruction?
-
What other symptoms are there, such as blue skin color, wheezing, high-pitched sound when breathing (stridor), coughing or sore throat?
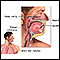
Stridor
Stridor is an abnormal, high-pitched, musical breathing sound. It is caused by a blockage in the throat or voice box (larynx). It is most often hea...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Has anything been breathed into the airway?
Tests that may be done include:
- Arterial blood gases
Arterial blood gases
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
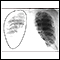
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen level
Reviewed By
Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Brown CA, Walls RM. Airway. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 1.
Rodrigues KK, Roosevelt GE. Acute inflammatory upper airway obstruction (croup, epiglottitis, laryngitis, and bacterial tracheitis). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 433.
Stephany A. Respiratory distress. In: Kliegman RM, Toth H, Bordini BJ, Basel D, eds. Nelson Pediatric Symptom-Based Diagnosis. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 4.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.



