Uric acid - blood
Uric acid is a chemical created when the body breaks down substances called purines. Purines are normally produced in the body and are also found in some foods and drinks. Foods with a high content of purines include liver, anchovies, mackerel, red meat, shellfish, dried beans and peas, and beer.
Most uric acid dissolves in blood and travels to the kidneys. From there, it passes out in urine. If your body produces too much uric acid or does not remove enough of it, you can get sick. A high level of uric acid in the blood is called hyperuricemia.
This test checks to see how much uric acid you have in your blood. Another test that can be used to check the level of uric acid is a test of your urine.
Uric acid is a test of your urine
The uric acid urine test measures the level of uric acid in the urine. The uric acid blood level can be checked using a blood test.
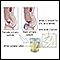
How the Test is Performed
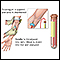
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
Drawn from a vein
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.
How to Prepare for the Test
You should not eat or drink anything for 4 hours before the test unless told otherwise.
Many medicines can interfere with blood test results.
- Your health care provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to see if you have a high level of uric acid in your blood. High levels of uric acid can sometimes cause gout or kidney disease.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis. It occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood and causes inflammation in the joints. Acute gout is a painful conditio...

You may have this test if you have had or are about to have certain types of chemotherapy. Rapid destruction of cancerous cells or weight loss, which may occur with such treatments, can rapidly increase the amount of uric acid in your blood.
Normal Results
Normal values are 3.0 to 7.1 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for women and 4.0 to 8.6 mg/dL for men.
For patients being treated for gout, the goal uric acid is either less than 6 mg/dL or 5 mg/dL based on clinical factors.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The example above shows the common measurement range for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Greater-than-normal levels of uric acid (hyperuricemia) may be due to:
- Acidosis
Acidosis
Acidosis is a condition in which there is too much acid in the body fluids. It is the opposite of alkalosis (a condition in which there is too much ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Alcohol (ethanol) consumption
- Chemotherapy-related side effects
- Dehydration
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive exercise
- Fructose consumption
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis refers to lactic acid build up in the bloodstream. Lactic acid is produced when oxygen levels become low in cells within the areas o...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Lead poisoning
Lead poisoning
Lead is a very strong poison. When a person swallows an object that has lead in it or breathes in lead dust, some of the poison can stay in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines such as cyclosporine, diuretics, nicotinic acid, salicylates (low dose), tacrolimus
- Medullary cystic kidney disease
- Obesity
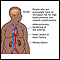
Obesity
Obesity means weighing more than what is healthy for a given height. Obesity is a serious, chronic disease. It can lead to other health problems, i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a bone marrow disease that leads to an abnormal increase in the number of blood cells. The red blood cells are the most af...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Psoriasis
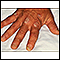
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Purine-rich diet
- Renal failure
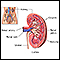
Renal failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Toxemia of pregnancy
Toxemia of pregnancy
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vitamin B12 deficiency
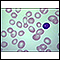
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Lower-than-normal levels of uric acid may be due to:
- Fanconi syndrome
Fanconi syndrome
Fanconi syndrome is a disorder of the kidney tubes in which certain substances normally absorbed into the bloodstream by the kidneys are released int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hereditary diseases of metabolism
- HIV infection
HIV infection
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low purine diet
- Medicines such as atorvastatin, captopril, enalapril, fenofibrate, losartan, probenecid, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic ...
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is a condition in which the body makes too much antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Other reasons this test may be performed include:
- Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) usually causes the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gout
- Injury of the kidney and ureter
Injury of the kidney and ureter
Injury to the kidney and ureter is damage to the organs of the upper urinary tract.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis)
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Dalbeth N. Clinical features and treatment of gout. In: Firestein GS, McInnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 97.
Edwards NL. Crystal deposition diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 252.
Weisbord SD, Palevsky PM. Prevention and management of acute kidney injury. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 29.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.



