ALP isoenzyme test
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme found in many body tissues such as the liver, bile ducts, bones, and intestine. There are several different structural forms of ALP called isoenzymes. The structure of the enzyme depends on where in the body it is produced. This test is most often used to test ALP made in the tissues of the liver and bones.
The ALP isoenzyme test is a lab test that measures the amounts of different types of ALP in the blood.
The ALP test is a related test.
ALP test
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a protein found in all body tissues. Tissues with higher amounts of ALP include the liver, bile ducts, and bone. A blo...
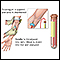
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
Drawn from a vein
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
Many medicines can interfere with blood test results.
- Your health care provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn.
Why the Test is Performed
When the ALP test result is high, you may need to have the ALP isoenzyme test. This test will help determine what part of the body is causing higher ALP levels.
This test may be used to diagnose or monitor:
- Bone disease
- Liver, gallbladder, or bile duct disease
Liver
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pain in the abdomen
- Parathyroid gland disease
- Vitamin D deficiency
It may also be done to check liver function and to see how medicines you take may affect your liver.
Normal Results
The normal value for total ALP is 44 to 147 international units per liter (IU/L) or 0.73 to 2.45 microkatal per liter (µkat/L). ALP isoenzyme testing may have differing normal values.
Adults have lower levels of ALP than children. Bones that are still growing produce higher levels of ALP. During some growth spurts, levels can be as high as 500 IU/L or 8.35 µkat/L. For this reason, the test is usually not done in children, and abnormal results refer to adults.
The isoenzyme test results can reveal whether the increase is in "bone" ALP or "liver" ALP.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The example above shows the common measurement range for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher-than-normal ALP levels:
- Biliary obstruction
- Bone disease
- Eating a fatty meal if you have blood type O or B
- Healing bone fracture
- Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which 1 or more of the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver disease
- Lymphoma
- Osteoblastic bone tumors
- Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones. It most often occurs because of a problem that leads to vitamin D deficiency, which helps your body absorb c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Paget disease of bone
Paget disease
Paget disease is a disorder that involves abnormal bone destruction and regrowth. This results in deformity of the affected bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Lower-than-normal levels of ALP:
- Hypophosphatasia
- Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that occurs when your body does not get enough nutrients.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Protein deficiency
Protein
Proteins are the building blocks of life. Every cell in the human body contains protein. The basic structure of protein is a chain of amino acids. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wilson disease
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Zinc deficiency
Levels that are only slightly higher than normal may not be a problem unless there are other signs of a disease or medical problem.
Other conditions for which the test may be done:
- Alcoholic liver disease (hepatitis/cirrhosis)
- Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Biliary stricture
Biliary stricture
A bile duct stricture is an abnormal narrowing, most often of the common bile duct. This is a tube that moves bile from the liver to the small intes...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gallstones
- Giant cell (temporal, cranial) arteritis
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) II
Multiple endocrine neoplasia, type II (MEN II) is a disorder passed down through families in which one or more of the endocrine glands are overactive...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pancreatitis
- Renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer that starts in the lining of very small tubes (tubules) in the kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gall bladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 141.
Korenblat KM. Approach to the patient with jaundice or abnormal liver tests. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 133.
Martin P. Approach to the patient with liver disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 132.
Weinstein RS. Osteomalacia and rickets. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 226.
Disclaimer
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.



