Alpha fetoprotein

Blood test
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver and yolk sac of a developing baby during pregnancy. AFP levels go down soon after birth. It is likely that AFP has no normal function in adults.
A test can be done to measure the amount of AFP in your blood.
How the Test is Performed
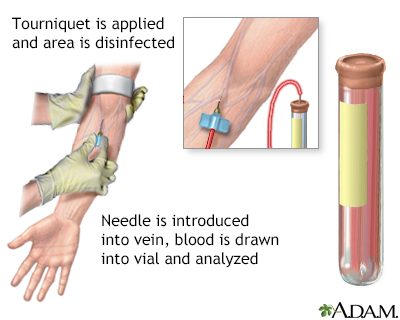
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is typically drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
How to Prepare for the Test
You do not need to take any special steps to prepare.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn.
Why the Test is Performed
Your health care provider may order this test to:
- Screen for problems in the baby during pregnancy. (The test is done as part of a larger set of blood tests called quadruple screen.)
- Diagnose certain liver disorders.
- Screen for and monitor some cancers.
Normal Results
The normal values in males or nonpregnant females are 0.7 to 9.3 ng/mL (0.7 to 9.3 µg/L).
The examples above are common measurements for results of these tests. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Greater than normal levels of AFP may be due to:
- Cancer in testes, ovaries, biliary (liver secretion) tract, stomach, or pancreas
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Liver cancer
- Malignant teratoma
- Recovery from hepatitis
- Problems during pregnancy
- Multiple gestation
References
Dugoff L, Wapner RJ. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 30.
Lee P, Jain S, Pincus MR, et al. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serologic and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 76.
Russo ML, Mahoney R, Driscoll DA, Al-Kouatly H. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 12.
Review Date: 8/18/2025
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.