Bilirubin - urine

Definition
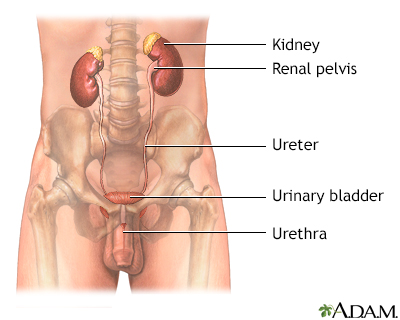
Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, which is a fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
This article is about a lab test to measure the amount of bilirubin in the urine. Large amounts of bilirubin in the body can lead to jaundice or yellowing of the skin.
Bilirubin may also be measured with a blood test.
How the Test is Performed
This test can be done on any urine sample.
For an infant, thoroughly wash the area where urine exits the body.
- Open a urine collection bag (a plastic bag with an adhesive paper on one end).
- For males, place the entire penis in the bag and attach the adhesive to the skin.
- For females, place the bag over the labia.
- Diaper as usual over the secured bag.
This procedure may take a few tries. An active baby can move the bag, causing urine to go into the diaper.
Check the infant often and change the bag after the infant has urinated into it. Drain the urine from the bag into the container provided by your health care provider.
Deliver the sample to the laboratory or to your provider as soon as possible.
How to Prepare for the Test
Many medicines can interfere with blood test results.
- Your provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- Do not stop or change your medicines without first talking to your provider.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination, and there is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
This test may be done to diagnose liver or gallbladder problems.
Normal Results
Bilirubin is not normally found in the urine.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Increased levels of bilirubin in the urine may be due to:
- Biliary tract disease, including gallstones in the biliary tract
- Cirrhosis, hepatitis, or other forms of liver disease
- Tumors of the liver or gallbladder
Considerations
Bilirubin can break down in light. That is why babies with jaundice are sometimes placed under blue fluorescent lamps.
References
Korenblat KM. Approach to the patient with jaundice or abnormal liver tests. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 133.
Krishnan A, Levin A. Laboratory assessment of kidney disease: glomerular filtration rate, urinalysis, and proteinuria. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 23.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
Review Date: 7/13/2025
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.