Small intestine aspirate and culture

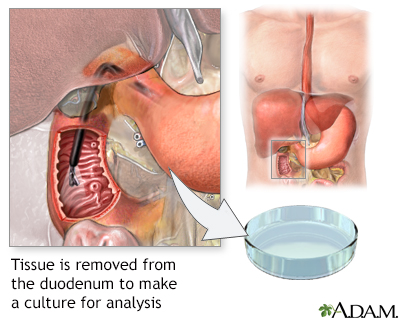
Duodenal tissue culture
Schedule an Appointment
Definition
Small intestine aspirate and culture is a lab test to check for infection in the small intestine.
How the Test is Performed
A sample of fluid from the small intestine is needed. A sample is taken during an upper endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, also called an EGD).
The fluid is placed in a special dish in the laboratory. It is watched for growth of bacteria or other organisms. This is called a culture.
How the Test will Feel
You are not involved in the test once the sample is taken.
Why the Test is Performed
Your health care provider may order this test if you have signs of too much bacteria growing in the intestinal tract. In most cases, other tests are done first. This test is rarely done outside of a research setting. In most cases, it has been replaced by a breath test that checks for excess bacteria in the small bowel.
Normally, small amounts of bacteria are present in the small intestine and they do not cause disease. However, the test may be done when your provider suspects that excess growth of intestinal bacteria is causing diarrhea.
Normal Results
No bacteria should be found.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be a sign of infection.
Risks
There are no risks associated with a laboratory culture. The risks of the EGD procedure include:
- Bleeding
- Perforation of (poking a hole in) the gastrointestinal tract by the scope
- Infection
Some people may not be able to have this test because of other medical conditions.
References
Höegenauer C, Hammer HF. Maldigestion and malabsorption. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 104.
Lacy BE, DiBaise JK. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 105.
Mathison BA, Pritt BS. Medical parasitology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 126.
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.