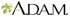Vesicles

Definition
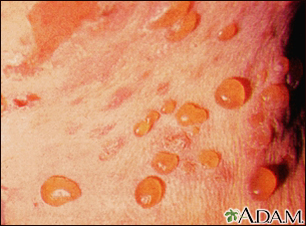
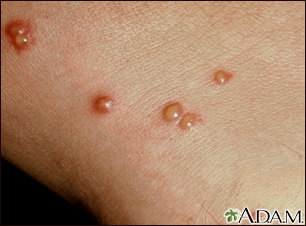
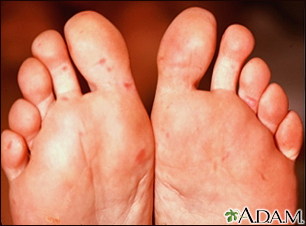
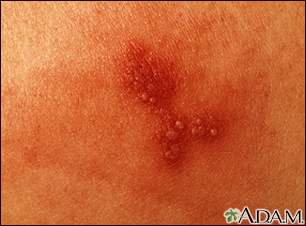
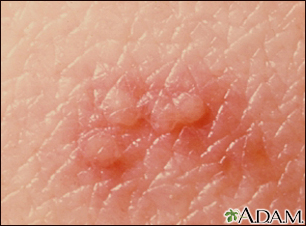
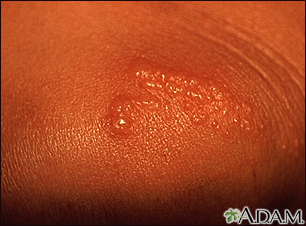
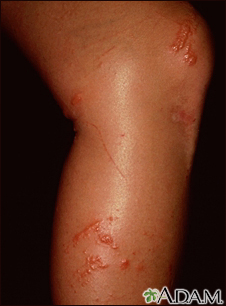
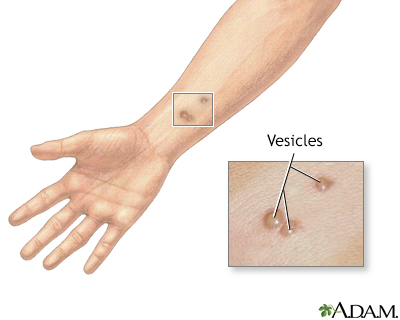
A vesicle is a small fluid-filled blister on the skin.
Considerations
A vesicle is small. It may be as tiny as the top of a pin or up to 0.20 inches (in) or 5 millimeters (mm) wide. A larger blister is called a bulla.
In many cases, vesicles break easily and release their fluid onto the skin. When this fluid dries, yellow crusts may remain on the skin surface.
Causes
Many diseases and conditions can cause vesicles. Common examples include:
- Allergic reactions to medicines
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
- Autoimmune disorders such as bullous pemphigoid or pemphigus
- Blistering skin diseases including porphyria cutanea tarda and dermatitis herpetiformis
- Chickenpox
- Contact dermatitis (such as due to poison ivy)
- Herpes simplex (cold sores, genital herpes)
- Herpes zoster (shingles)
- Bacterial infections
- Fungal infections
- Burns
- Friction
- Treatment with cryotherapy (to treat a wart, for example)
Home Care
It is best to have your health care provider examine any skin rashes, including vesicles.
Over-the-counter treatments are available for certain conditions that cause vesicles, including poison ivy and cold sores.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have any unexplained blisters on your skin.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will look at your skin. Some vesicles can be diagnosed simply by how they look.
In many cases, additional tests are needed. The fluid inside a blister may be sent to a lab for closer examination. In particularly difficult cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to make or confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment will depend on the cause of the vesicles.
References
Dinulos JGH. Vesicular and bullous diseases. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
James WD. Cutaneous signs and diagnosis. In: James WD, ed. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 2.
Kroshinsky D. Macular, papular, purpuric, vesiculobullous, and pustular diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 406.
Review Date: 6/3/2025
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language.
© 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures.