Multimedia Gallery





Knee arthroscopy - series
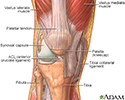
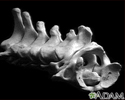
Knee arthroscopy - series - Normal anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of the distal end of the femur (femoral condyles) and the proximal end of the tibia (tibial plateau). A number of ligaments run between the femur and the tibia in the knee joint. The anterior cruciate ligament, the posterior cruciate ligament, and the meniscal ligaments are among the ligaments of the knee joint.
Knee arthroscopy - series
Knee arthroscopy - series - Normal anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of the distal end of the femur (femoral condyles) and the proximal end of the tibia (tibial plateau). A number of...
Knee arthroscopy - series
Indications
Injury to the ligaments of the knee are common sports-related injuries.
Arthroscopy, which involves the use of a small camera and small instruments on the end of long narrow tubes, introduced into the knee through small incisions, may be recommended for knee problems such as:
- A torn knee disc (meniscus)
- A damaged knee bone (patella)
- A damaged ligament
- Inflamed or damaged lining of the joint (synovium)
Knee arthroscopy - series
Indications
Injury to the ligaments of the knee are common sports-related injuries.Arthroscopy, which involves the use of a small camera and small instruments on...
Knee arthroscopy - series
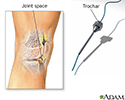
Procedure, part 1
Several small punctures are made into the knee joint while the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia) or sleepy (sedated) and pain-free (regional anesthesia or spinal anesthesia).
Knee arthroscopy - series
Procedure, part 1
Several small punctures are made into the knee joint while the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia) or sleepy (sedated) and pain...
Knee arthroscopy - series
Procedure, part 2
The viewing scope (arthroscope) and other instruments are inserted into the knee joint. The surgeon can see the ligaments, the knee disc (meniscus), the knee bone (patella), the lining of the joint (synovium), and the rest of the joint. Damaged tissues can be removed. Arthroscopy can also be used to help view the inside of the knee while ligaments or tendons are repaired from the outside.
Knee arthroscopy - series
Procedure, part 2
The viewing scope (arthroscope) and other instruments are inserted into the knee joint. The surgeon can see the ligaments, the knee disc (meniscus), ...
Knee arthroscopy - series
Aftercare
Patients are usually able to leave the hospital after arthroscopic knee surgery within 24 hours of surgery. The recovery time, and the need for physical therapy after surgery are determined by the injury treated and the procedure performed.
Knee arthroscopy - series
Aftercare
Patients are usually able to leave the hospital after arthroscopic knee surgery within 24 hours of surgery. The recovery time, and the need for physi...
Review Date: 6/4/2025
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The knee is a complex joint made up of the distal end of the femur (femoral condyles) and the proximal end of the tibia (tibial plateau). A number of ligaments run between the femur and the tibia in the knee joint. The anterior cruciate ligament, the posterior cruciate ligament, and the meniscal ligaments are among the ligaments of the knee joint.
Injury to the ligaments of the knee are common sports-related injuries.
Arthroscopy, which involves the use of a small camera and small instruments on the end of long narrow tubes, introduced into the knee through small incisions, may be recommended for knee problems such as:
- A torn knee disc (meniscus)
- A damaged knee bone (patella)
- A damaged ligament
- Inflamed or damaged lining of the joint (synovium)
Several small punctures are made into the knee joint while the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia) or sleepy (sedated) and pain-free (regional anesthesia or spinal anesthesia).
The viewing scope (arthroscope) and other instruments are inserted into the knee joint. The surgeon can see the ligaments, the knee disc (meniscus), the knee bone (patella), the lining of the joint (synovium), and the rest of the joint. Damaged tissues can be removed. Arthroscopy can also be used to help view the inside of the knee while ligaments or tendons are repaired from the outside.
Patients are usually able to leave the hospital after arthroscopic knee surgery within 24 hours of surgery. The recovery time, and the need for physical therapy after surgery are determined by the injury treated and the procedure performed.





Animations
- Ankle ligament injury
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Anterior shoulder stretch
- Arm reach
- Arthritis
- Bone fracture repair
- Bunion
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Exercise
- External rotation with band
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot pain
- Heel pain
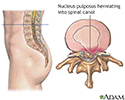
- Herniated disk
- Herniated nucleus pulposus ...
- Hip joint replacement
- How to use a pill cutter
- Internal rotation with band
- Isometric
- Knee joint replacement
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neck pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis
- Pendulum exercise
- Plantar fasciitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff problems
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Shoulder blade retraction
- Shoulder blade retraction w...
- Shoulder joint dislocation
- Shoulder pain
- Spinal stenosis
- Stretching back of your shoulder
- Up the back stretch
- Vacation health care
- Wall push-up
- Wall stretch
- What is tennis elbow?
Illustrations
- ACL degrees
- ACL injury
- Active vs. inactive muscle
- Aerobic exercise
- Ankle anatomy
- Ankle sprain
- Ankle sprain swelling
- Anterior cruciate ligament ...
- Anterior skeletal anatomy
- Arthritis in hip
- Aseptic necrosis
- Baker cyst
- Benefit of regular exercise
- Blood supply to bone
- Blood test
- Bone biopsy
- Bone density scan
- Bone graft harvest
- Bone tumor
- Bone-building exercise
- Bursa of the elbow
- Bursa of the knee
- Bursitis of the shoulder
- Calcium benefit
- Calcium source
- Calculating body frame size
- Calories and fat per serving
- Carpal biopsy
- Carpal tunnel surgical procedure
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cauda equina
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cervical spondylosis
- Cervical vertebrae
- Changes in spine with age
- Chest stretch
- Chondromalacia of the patella
- Clubfoot deformity
- Colles fracture
- Common peroneal nerve dysfu...
- Compression fracture
- Compression of the median nerve
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Contracture deformity
- Corns and calluses
- CREST syndrome
- CT scan
- Damaged axillary nerve
- Dislocation of the hip
- Early treatment of injury
- Elbow - side view
- Electromyography
- Ewing sarcoma - x-ray
- Exercise - a powerful tool
- Exercise and age
- Exercise and heart rate
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- Exercise with friends
- External fixation device
- Fast food
- Femoral fracture
- Femoral nerve damage
- Fibromyalgia
- Fish in diet
- Foot swelling
- Forward bend test
- Fracture types (1)
- Fracture types (2)
- Fracture, forearm - x-ray
- Fractures across a growth plate
- Groin stretch
- Hammer toe
- Hamstring stretch
- Head trauma
- Healthy diet
- Herniated disk repair
- Herniated lumbar disk
- Herniated nucleus pulposus
- Hip fracture
- Hip stretch
- Hunger center in brain
- Hypermobile joints
- Impingement syndrome
- Inflamed Achilles tendon
- Inflamed shoulder tendons
- Internal fixation devices
- Intervertebral disk
- Isometric exercise
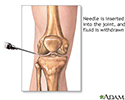
- Joint aspiration
- Knee arthroscopy
- Knee joint
- Knee joint replacement pros...
- Knee pain
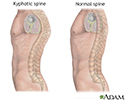
- Kyphosis
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Lateral collateral ligament...
- Lateral collateral ligament pain
- Leg pain (Osgood-Schlatter)
- Leg skeletal anatomy
- Limited range of motion
- Location of whiplash pain
- Lordosis
- Lower leg edema
- Lower leg muscles
- Lower leg muscles
- Lumbar vertebrae
- Lupus - discoid on a child'...
- Lupus - discoid on the face
- Lupus, discoid - view of l...
- Medial collateral ligament
- Medial collateral ligament ...
- Medial collateral ligament pain
- Meniscal tears
- Metatarsus adductus
- MRI scans
- Muscle biopsy
- Muscle cells vs. fat cells
- Muscle pain
- Muscle strain
- Muscular atrophy
- myPlate
- Neck pain
- Nerve biopsy
- Nerve conduction test
- Normal foot x-ray
- Normal knee anatomy
- Nuclear scan
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis vs. rheumato...
- Osteogenic sarcoma - x-ray
- Osteomyelitis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis
- Patellar dislocation
- Physical activity - prevent...
- Plantar fascia
- Plantar fasciitis
- Posterior cruciate ligament...
- Posterior spinal anatomy
- Psoriasis - guttate on the ...
- Psoriasis - guttate on the cheek
- Radial head injury
- Radial nerve dysfunction
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Reactive arthritis - view o...
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff muscles
- Runners knee
- Sacrum
- Sciatic nerve
- Sciatic nerve damage
- Sclerodactyly
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis brace
- Shin splints
- Shoulder arthroscopy
- Shoulder joint
- Shoulder joint inflammation
- Shoulder sling
- Signs of scoliosis
- Skeletal spine
- Skeleton
- Smashed fingers
- Spinal anatomy
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal curves
- Spinal fusion
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal tumor
- Spine supporting structures
- Sprained ankle
- Superficial anterior muscles
- Surface anatomy - normal palm
- Surface anatomy - normal wrist
- Synovial biopsy
- Synovial fluid
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Systemic lupus erythematosu...
- Tailbone (coccyx)
- Telangiectasia
- Tendinitis
- Tendon vs. ligament
- Tendonitis
- Tendons and muscles
- The structure of a joint
- Thigh stretch
- Tibial nerve
- Tophi gout in hand
- Torn lateral collateral ligament
- Torn medial collateral ligament
- Torticollis (wry neck)
- Treatment for leg strain
- Triangular shoulder sling
- Triceps stretch
- Ulnar nerve damage
- Uric acid crystals
- Vertebra, cervical (neck)
- Vertebra, lumbar (low back)
- Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
- Vertebrae
- Vertebral column
- Vitamin D source
- Weight loss
- Whiplash
- Wrist anatomy
- Wrist splint
- X-ray
- X-ray
- Yo-yo dieting
Presentations
- Ankle sprain - Series
- Anterior cruciate ligament ...
- Bone fracture repair - series
- Bunion removal - series
- Carpal tunnel repair - series
- Clubfoot repair - series
- Creating a sling - series
- Hand splint - series
- Hip joint replacement - series
- Knee arthroscopy - series
- Knee joint replacement - series
- Leg lengthening - series
- Lumbar spinal surgery - series
- Microdiskectomy - series
- Partial knee replacement - ...
- Rotator cuff repair - series
- Shoulder separation - series
- Spinal bone graft - series
- Spinal fusion - series
- Spinal surgery - cervical -...
- Two person roll - series

 Bookmark
Bookmark