Multimedia Gallery






Pancreas transplant - series
Pancreas transplant - series
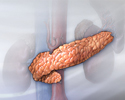
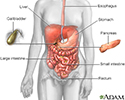
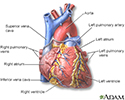
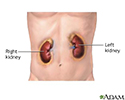
The pancreas resides in the back of the abdomen. It functions to produce digestive enzymes which are delivered to the small intestine (duodenum) and various hormones, which are delivered to the bloodstream. One of the most important hormones produced by the pancreas is insulin. Insulin is produced by specialized cells of the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
Pancreas transplant - series
Pancreas transplant - series
The pancreas resides in the back of the abdomen. It functions to produce digestive enzymes which are delivered to the small intestine (duodenum) and ...
Pancreas transplant - series
Indications
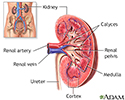
One of the most common diseases which affects the pancreas is insulin dependent diabetes, or type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the result of an autoimmune attack on the islet cells which produce insulin. The resultant lack of insulin leads to excess blood sugar levels in the blood and a variety of health problems including visual disturbances (diabetic retinopathy), heart disease, nerve disorders (diabetic neuropathy), and kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy). Diabetic patients must take insulin everyday.
Pancreas transplant - series
Indications
One of the most common diseases which affects the pancreas is insulin dependent diabetes, or type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the result of an aut...
Pancreas transplant - series
Incision
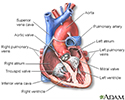
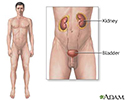
Pancreas transplant is a procedure in which a donor pancreas, obtained from a brain-dead organ donor who is maintained on life support, is surgically implanted into a diabetic patient. This operation is most often done in combination with kidney transplant in a patient who have diabetes and kidney failure as a result of their diabetes. The recipient's own diseased pancreas is left in place and the donor pancreas transplanted through a midline abdominal incision.
Pancreas transplant - series
Incision
Pancreas transplant is a procedure in which a donor pancreas, obtained from a brain-dead organ donor who is maintained on life support, is surgically...
Pancreas transplant - series
Procedure, part 1
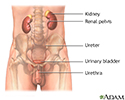
The donor duodenum, which remains attached to the donor pancreas, is attached to the recipient's small bowel to allow the digestive enzymes produced by the donor pancreas to drain into the small intestine.
Pancreas transplant - series
Procedure, part 1
The donor duodenum, which remains attached to the donor pancreas, is attached to the recipient's small bowel to allow the digestive enzymes produced ...
Pancreas transplant - series
Procedure, part 2
The vessels of the donor pancreas are attached to the vessels in the groin that supply the leg.
Pancreas transplant - series
Procedure, part 2
The vessels of the donor pancreas are attached to the vessels in the groin that supply the leg.
Pancreas transplant - series
Aftercare
Attempts have been made to isolate only the insulin producing islets from the donor pancreas and infuse these islets directly into the bloodstream of diabetic patients, where they would lodge in the tissues and produce insulin. While still an experimental procedure, "islet transplantation" may someday offer a treatment for diabetes that, unlike pancreas transplant, does not require a major surgery.
Pancreas transplant - series
Aftercare
Attempts have been made to isolate only the insulin producing islets from the donor pancreas and infuse these islets directly into the bloodstream of...
Review Date: 7/9/2025
Reviewed By: John Meilahn, MD, General Surgeon, Wyndmoor, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The pancreas resides in the back of the abdomen. It functions to produce digestive enzymes which are delivered to the small intestine (duodenum) and various hormones, which are delivered to the bloodstream. One of the most important hormones produced by the pancreas is insulin. Insulin is produced by specialized cells of the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
One of the most common diseases which affects the pancreas is insulin dependent diabetes, or type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the result of an autoimmune attack on the islet cells which produce insulin. The resultant lack of insulin leads to excess blood sugar levels in the blood and a variety of health problems including visual disturbances (diabetic retinopathy), heart disease, nerve disorders (diabetic neuropathy), and kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy). Diabetic patients must take insulin everyday.
Pancreas transplant is a procedure in which a donor pancreas, obtained from a brain-dead organ donor who is maintained on life support, is surgically implanted into a diabetic patient. This operation is most often done in combination with kidney transplant in a patient who have diabetes and kidney failure as a result of their diabetes. The recipient's own diseased pancreas is left in place and the donor pancreas transplanted through a midline abdominal incision.
The donor duodenum, which remains attached to the donor pancreas, is attached to the recipient's small bowel to allow the digestive enzymes produced by the donor pancreas to drain into the small intestine.
The vessels of the donor pancreas are attached to the vessels in the groin that supply the leg.
Attempts have been made to isolate only the insulin producing islets from the donor pancreas and infuse these islets directly into the bloodstream of diabetic patients, where they would lodge in the tissues and produce insulin. While still an experimental procedure, "islet transplantation" may someday offer a treatment for diabetes that, unlike pancreas transplant, does not require a major surgery.






Animations
- Blood pressure
- Bunion
- Cataract
- Childhood obesity
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Coronary artery disease
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Diabetes - retinal conditions
- Diabetes and risk of seriou...
- Dialysis
- Erection problems
- Exercise
- Foot pain
- Gallstones
- Glaucoma
- Hardening of arteries
- HbA1c
- Healthy Guide to Fast Food
- Heart attack
- Hypertension
- Hypertension - overview
- Immune response
- Smoking
- Smoking tips to quit
- Stroke
- Stroke
- The goals of proper type 2 ...
- Tobacco use - effects on ar...
- Tracking your blood pressur...
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary tract infection - adults
- Vaccines
- Venous insufficiency
Illustrations
- 15/15 rule
- Abdominal girth measurement
- Abdominal muscles
- Acanthosis nigricans - close-up
- Acanthosis nigricans on the hand
- Acute MI
- Adjustable gastric banding
- Aerobic exercise
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Angina
- Anterior heart arteries
- Atherosclerosis of the extr...
- Autonomic Nerves
- Baby bottle tooth decay
- Benefit of regular exercise
- Biguanides
- Blood pressure
- Blood pressure check
- Blood test
- Blood test
- Brain
- Brainstem function
- Calculating body frame size
- Candida - fluorescent stain
- Candidiasis, cutaneous - ar...
- Carotid dissection
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cataract - close-up of the eye
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cerebellum - function
- Childhood obesity
- Children's diets
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol producers
- Circle of Willis
- Circulation of blood throug...
- Complex carbohydrates
- Coronary artery blockage
- Coronary artery disease
- Creatinine tests
- DASH diet
- Dermatitis - reaction to tinea
- Dermatitis - stasis on the leg
- Developmental process of at...
- Diabetes and exercise
- Diabetes and nerve damage
- Diabetes risk factors
- Diabetic blood circulation ...
- Diabetic emergency supplies
- Diabetic foot care
- Diabetic foot care
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Different types of weight gain
- Digestive system
- Endarterectomy
- Endocrine glands
- Energy levels
- Exercise - a powerful tool
- Exercise 30 minutes a day
- Exercise and age
- Exercise and heart rate
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- Exercise with friends
- Eye
- Fast food
- Fasting plasma glucose test
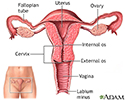
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female urinary tract
- Femoral nerve damage
- Fish in diet
- Flexibility exercise
- Follicle development
- Folliculitis - decalvans on...
- Folliculitis on the leg
- Food and insulin release
- Food label guide for candy
- Food label guide for whole ...
- Foot swelling
- Fruits and vegetables
- Fungus
- Gestational diabetes
- Gingivitis
- Gingivitis
- Glaucoma
- Glucose in blood
- Glucose test
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Granuloma annulare - close-up
- Granuloma annulare on the elbow
- Granuloma annulare on the eyelid
- Granuloma annulare on the legs
- Hair follicle anatomy
- Hammer toe
- Healthy diet
- Healthy diet
- Heart - front view
- Heart - section through the...
- Heart attack symptoms
- High blood pressure tests
- Influenza
- Influenza vaccines
- Ingrown toenail
- Insulin production and diabetes
- Insulin pump
- Insulin pump
- Islets of Langerhans
- Isometric exercise
- Jaw pain and heart attacks
- Kidney - blood and urine flow
- Kidney anatomy
- Kidneys
- Left cerebral hemisphere - ...
- Lifestyle changes
- Lipocytes (fat cells)
- Low blood sugar symptoms
- Male urinary system
- Male urinary tract
- Monitoring blood pressure
- myPlate
- Nail infection - candidal
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Nervous system
- Nervous system
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Obesity and health
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Osmolality test
- Pancreas
- Pancreas and kidneys
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Pesticides and fruit
- Pharmacy options
- Physical activity - prevent...
- Pituitary and TSH
- Plaque buildup in arteries
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Post myocardial infarction ...
- Posterior heart arteries
- Prevention of heart disease
- Progressive build-up of pla...
- Proteins
- Quitting smoking
- Radial nerve dysfunction
- Read food labels
- Retinal dye injection
- Right cerebral hemisphere -...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea manuum on ...
- Ringworm - tinea on the han...
- Ringworm of the scalp
- Ringworm, tinea capitis - c...
- Roux-en-Y stomach surgery f...
- Salad nutrients
- Saturated fats
- Secondary infection
- Simple carbohydrates
- Slit-lamp exam
- Smoking hazards
- Sources of fiber
- Soy
- Stable angina
- Starchy foods
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Stomach
- Stomach disease or trauma
- Stye
- Sulfonylureas drug
- Surface anatomy - normal palm
- Surface anatomy - normal wrist
- Swollen gums
- Thiazolidinediones
- Thyroid uptake test
- Tinea corporis - ear
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - shoulders
- Tinea versicolor on the back
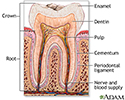
- Tooth anatomy
- Tooth anatomy
- Trans fatty acids
- Type I diabetes
- Ulnar nerve damage
- Untreated hypertension
- Urine sample
- Uterus
- Vaginal discharge
- Visual field test
- Vitiligo
- Vitiligo - drug induced
- Vitiligo on the back and arm
- Vitiligo on the face
- Weight loss
- White nail syndrome
- Wood's lamp test - of the scalp
- Wrist anatomy
- Xerosis - close-up
- Yeast and mold
- Yeast infections
- Yoga
- Yo-yo dieting

 Bookmark
Bookmark