Multimedia Gallery









Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - Series
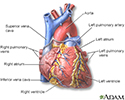
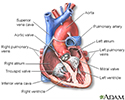
The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. The right coronary artery supplies both the left and the right heart; the left coronary artery supplies the left heart.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - Series
The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. The right coronary artery supplies both the left and the right heart; the left coronary arter...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Indication
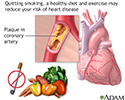
Fat and cholesterol accumulates on the inside of arteries (atherosclerosis). The small arteries of the heart muscle (the coronary arteries) can be narrowed or blocked by this accumulation. If the narrowing is small, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, or PTCA for short, may be the course for treatment. PTCA is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle. The indications for PTCA are:
- Persistent chest pain (angina)
- Blockage of only one or two coronary arteries
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Indication
Fat and cholesterol accumulates on the inside of arteries (atherosclerosis). The small arteries of the heart muscle (the coronary arteries) can be na...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 1
While the patient is awake and pain-free (local anesthesia), a catheter is inserted into an artery at the top of the leg (the femoral artery). The procedure begins with the doctor injecting some local anesthesia into the groin area and putting a needle into the femoral artery (the blood vessel that runs from the heart down the leg). Once the needle is inserted, a guide wire is placed through the needle, into the blood vessel. Following this step, the guide wire is left in the blood vessel and the needle is removed. A large needle called an introducer is then placed over the guide wire and the guide wire is removed.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 1
While the patient is awake and pain-free (local anesthesia), a catheter is inserted into an artery at the top of the leg (the femoral artery). The pr...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 2
Next, a diagnostic catheter, which is a long narrow tube, is advanced through the introducer over a .035 inch (.0889 cm) guidewire, into the blood vessel. This catheter is then guided to the aorta and the guidewire is removed. Once the catheter is placed in the opening or ostium of one of the coronary arteries, the doctor injects dye and takes a series of X-rays (film of the images).
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 2
Next, a diagnostic catheter, which is a long narrow tube, is advanced through the introducer over a .035 inch (.0889 cm) guidewire, into the blood ve...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 3
The first catheter is exchanged out over the guidewire for a guiding catheter and the guidewire is removed. A smaller guidewire is advanced across the blocked section of the coronary artery and a balloon-tipped tube is positioned so the balloon part of the tube is beside the blockage. The balloon is then inflated for a few seconds to compress the blockage against the artery wall. Then the balloon is deflated. The doctor may repeat this a few times, each time pumping up the balloon a little more to widen the passage for the blood to flow through. This treatment may be repeated at each blocked site in the coronary arteries.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 3
The first catheter is exchanged out over the guidewire for a guiding catheter and the guidewire is removed. A smaller guidewire is advanced across th...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 4
A device called a stent may be placed. A stent is a latticed, metal scaffold that is placed within the coronary artery to keep the vessel open.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 4
A device called a stent may be placed. A stent is a latticed, metal scaffold that is placed within the coronary artery to keep the vessel open.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 5
Once the catheter has been positioned at the coronary artery origin, contrast media is injected and a series of X-rays (film) are taken to check for any change in the arteries. Following this, the catheter is removed and the procedure is completed.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Procedure, part 5
Once the catheter has been positioned at the coronary artery origin, contrast media is injected and a series of X-rays (film) are taken to check for ...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Aftercare, part 1
This procedure can greatly improve the blood flow through the coronary arteries and to the heart tissue in about 90% of patients and may eliminate the need for coronary artery bypass surgery. The outcome is relief from chest pain symptoms and an improved exercise capacity. In 2 out of 3 cases, the procedure is considered successful with complete elimination of the narrowing or blockage.
This procedure treats the condition but does not eliminate the cause and recurrences happen in 1 out of 3 to 5 cases. Patients should consider diet, exercise, and stress reduction measures. If adequate widening of the narrowing is not accomplished, heart surgery (coronary artery bypass graft surgery, also called a CABG) may be recommended.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Aftercare, part 1
This procedure can greatly improve the blood flow through the coronary arteries and to the heart tissue in about 90% of patients and may eliminate th...
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Aftercare, part 2
Immediately after the procedure, a ten-pound (5 kg) sandbag may be placed over the femoral artery puncture site in the leg and remain there for 6 hours. This is done to help the artery heal.
Coronary artery balloon angioplasty - series
Aftercare, part 2
Immediately after the procedure, a ten-pound (5 kg) sandbag may be placed over the femoral artery puncture site in the leg and remain there for 6 hou...
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. The right coronary artery supplies both the left and the right heart; the left coronary artery supplies the left heart.
Fat and cholesterol accumulates on the inside of arteries (atherosclerosis). The small arteries of the heart muscle (the coronary arteries) can be narrowed or blocked by this accumulation. If the narrowing is small, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, or PTCA for short, may be the course for treatment. PTCA is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle. The indications for PTCA are:
- Persistent chest pain (angina)
- Blockage of only one or two coronary arteries
While the patient is awake and pain-free (local anesthesia), a catheter is inserted into an artery at the top of the leg (the femoral artery). The procedure begins with the doctor injecting some local anesthesia into the groin area and putting a needle into the femoral artery (the blood vessel that runs from the heart down the leg). Once the needle is inserted, a guide wire is placed through the needle, into the blood vessel. Following this step, the guide wire is left in the blood vessel and the needle is removed. A large needle called an introducer is then placed over the guide wire and the guide wire is removed.
Next, a diagnostic catheter, which is a long narrow tube, is advanced through the introducer over a .035 inch (.0889 cm) guidewire, into the blood vessel. This catheter is then guided to the aorta and the guidewire is removed. Once the catheter is placed in the opening or ostium of one of the coronary arteries, the doctor injects dye and takes a series of X-rays (film of the images).
The first catheter is exchanged out over the guidewire for a guiding catheter and the guidewire is removed. A smaller guidewire is advanced across the blocked section of the coronary artery and a balloon-tipped tube is positioned so the balloon part of the tube is beside the blockage. The balloon is then inflated for a few seconds to compress the blockage against the artery wall. Then the balloon is deflated. The doctor may repeat this a few times, each time pumping up the balloon a little more to widen the passage for the blood to flow through. This treatment may be repeated at each blocked site in the coronary arteries.
A device called a stent may be placed. A stent is a latticed, metal scaffold that is placed within the coronary artery to keep the vessel open.
Once the catheter has been positioned at the coronary artery origin, contrast media is injected and a series of X-rays (film) are taken to check for any change in the arteries. Following this, the catheter is removed and the procedure is completed.
This procedure can greatly improve the blood flow through the coronary arteries and to the heart tissue in about 90% of patients and may eliminate the need for coronary artery bypass surgery. The outcome is relief from chest pain symptoms and an improved exercise capacity. In 2 out of 3 cases, the procedure is considered successful with complete elimination of the narrowing or blockage.
This procedure treats the condition but does not eliminate the cause and recurrences happen in 1 out of 3 to 5 cases. Patients should consider diet, exercise, and stress reduction measures. If adequate widening of the narrowing is not accomplished, heart surgery (coronary artery bypass graft surgery, also called a CABG) may be recommended.
Immediately after the procedure, a ten-pound (5 kg) sandbag may be placed over the femoral artery puncture site in the leg and remain there for 6 hours. This is done to help the artery heal.









Animations
- Blood pressure
- Bunion
- Cataract
- Childhood obesity
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Coronary artery disease
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Diabetes - retinal conditions
- Diabetes and risk of seriou...
- Dialysis
- Erection problems
- Exercise
- Foot pain
- Gallstones
- Glaucoma
- Hardening of arteries
- HbA1c
- Healthy Guide to Fast Food
- Heart attack
- Hypertension
- Hypertension - overview
- Immune response
- Smoking
- Smoking tips to quit
- Stroke
- Stroke
- The goals of proper type 2 ...
- Tobacco use - effects on ar...
- Tracking your blood pressur...
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary tract infection - adults
- Vaccines
- Venous insufficiency
Illustrations
- 15/15 rule
- Abdominal girth measurement
- Abdominal muscles
- Acanthosis nigricans - close-up
- Acanthosis nigricans on the hand
- Acute MI
- Adjustable gastric banding
- Aerobic exercise
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Angina
- Anterior heart arteries
- Atherosclerosis of the extr...
- Autonomic Nerves
- Baby bottle tooth decay
- Benefit of regular exercise
- Biguanides
- Blood pressure
- Blood pressure check
- Blood test
- Blood test
- Brain
- Brainstem function
- Calculating body frame size
- Candida - fluorescent stain
- Candidiasis, cutaneous - ar...
- Carotid dissection
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cataract - close-up of the eye
- Central nervous system
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cerebellum - function
- Childhood obesity
- Children's diets
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol producers
- Circle of Willis
- Circulation of blood throug...
- Complex carbohydrates
- Coronary artery blockage
- Coronary artery disease
- Creatinine tests
- DASH diet
- Dermatitis - reaction to tinea
- Dermatitis - stasis on the leg
- Developmental process of at...
- Diabetes and exercise
- Diabetes and nerve damage
- Diabetes risk factors
- Diabetic blood circulation ...
- Diabetic emergency supplies
- Diabetic foot care
- Diabetic foot care
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Different types of weight gain
- Digestive system
- Endarterectomy
- Endocrine glands
- Energy levels
- Exercise - a powerful tool
- Exercise 30 minutes a day
- Exercise and age
- Exercise and heart rate
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- Exercise with friends
- Eye
- Fast food
- Fasting plasma glucose test
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female urinary tract
- Femoral nerve damage
- Fish in diet
- Flexibility exercise
- Follicle development
- Folliculitis - decalvans on...
- Folliculitis on the leg
- Food and insulin release
- Food label guide for candy
- Food label guide for whole ...
- Foot swelling
- Fruits and vegetables
- Fungus
- Gestational diabetes
- Gingivitis
- Gingivitis
- Glaucoma
- Glucose in blood
- Glucose test
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Granuloma - fungal (Majocchi's)
- Granuloma annulare - close-up
- Granuloma annulare on the elbow
- Granuloma annulare on the eyelid
- Granuloma annulare on the legs
- Hair follicle anatomy
- Hammer toe
- Healthy diet
- Healthy diet
- Heart - front view
- Heart - section through the...
- Heart attack symptoms
- High blood pressure tests
- Influenza
- Influenza vaccines
- Ingrown toenail
- Insulin production and diabetes
- Insulin pump
- Insulin pump
- Islets of Langerhans
- Isometric exercise
- Jaw pain and heart attacks
- Kidney - blood and urine flow
- Kidney anatomy
- Kidneys
- Left cerebral hemisphere - ...
- Lifestyle changes
- Lipocytes (fat cells)
- Low blood sugar symptoms
- Male urinary system
- Male urinary tract
- Monitoring blood pressure
- myPlate
- Nail infection - candidal
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Nervous system
- Nervous system
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Obesity and health
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Osmolality test
- Pancreas
- Pancreas and kidneys
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Pesticides and fruit
- Pharmacy options
- Physical activity - prevent...
- Pituitary and TSH
- Plaque buildup in arteries
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Post myocardial infarction ...
- Posterior heart arteries
- Prevention of heart disease
- Progressive build-up of pla...
- Proteins
- Quitting smoking
- Radial nerve dysfunction
- Read food labels
- Retinal dye injection
- Right cerebral hemisphere -...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea corporis o...
- Ringworm - tinea manuum on ...
- Ringworm - tinea on the han...
- Ringworm of the scalp
- Ringworm, tinea capitis - c...
- Roux-en-Y stomach surgery f...
- Salad nutrients
- Saturated fats
- Secondary infection
- Simple carbohydrates
- Slit-lamp exam
- Smoking hazards
- Sources of fiber
- Soy
- Stable angina
- Starchy foods
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Stomach
- Stomach disease or trauma
- Stye
- Sulfonylureas drug
- Surface anatomy - normal palm
- Surface anatomy - normal wrist
- Swollen gums
- Thiazolidinediones
- Thyroid uptake test
- Tinea corporis - ear
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - close-up
- Tinea versicolor - shoulders
- Tinea versicolor on the back
- Tooth anatomy
- Tooth anatomy
- Trans fatty acids
- Type I diabetes
- Ulnar nerve damage
- Untreated hypertension
- Urine sample
- Uterus
- Vaginal discharge
- Visual field test
- Vitiligo
- Vitiligo - drug induced
- Vitiligo on the back and arm
- Vitiligo on the face
- Weight loss
- White nail syndrome
- Wood's lamp test - of the scalp
- Wrist anatomy
- Xerosis - close-up
- Yeast and mold
- Yeast infections
- Yoga
- Yo-yo dieting

 Bookmark
Bookmark