Multimedia Gallery






Heart valve surgery - series
Heart valve surgery - Series
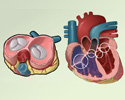
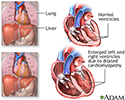
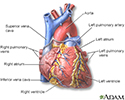
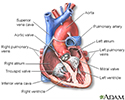
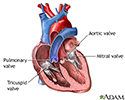
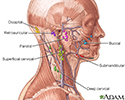
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the direction of blood flow through the heart. The opening and closing of the heart valves produce the heart-beat sounds.
Heart valve surgery - series
Heart valve surgery - Series
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the directio...
Heart valve surgery - series
Indications
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for:
- narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)
- leaking of the heart valve
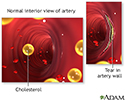
Valve problems may be caused by infections (rheumatic fever) or birth defects and may cause heart failure (congestive heart failure) and infections (infective endocarditis).
The surgery is done while the patient is deep-asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia). An incision is made through the breast bone (sternum).
Heart valve surgery - series
Indications
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for: narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)leaking of the heart valve Valve problems may be caused by inf...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 1
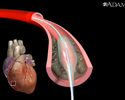
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood oxygenated and circulating while the heart is being operated on.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 1
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood ...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 2
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human donors (cadavers), modified natural valves are from animal donors (porcine: pigs) which are placed in synthetic rings, and artificial valves are made of metal or plastic. Natural valves rarely require life-long medication to prevent blood clot formation (anticoagulation), whereas artificial valves will require anticoagulation.
The advantage of mechanical valves is that they last longer-thus, the tradeoff of lifelong anticoagulation in some cases is worth it to avoid a second valve replacement surgery.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 2
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human ...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 3
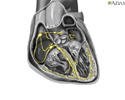
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 3
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
Heart valve surgery - series
Aftercare
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies depending on the heart valve and averages 2% to 5%. Approximately 2 out of 3 patients who received an artificial mitral valve are still alive 9 years after the surgery. Life-long anticoagulant therapy is necessary for patients with artificial heart valves. The clicking of the mechanical heart valve may be heard in the chest and is normal.
The first 2 or 3 days following the operation are spent in an intensive care unit where heart functions can be monitored constantly. The average hospital stay is 3 weeks. A few weeks to several months should be allowed for complete recovery, depending on health before surgery.
Heart valve surgery - series
Aftercare
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies dep...
Review Date: 1/27/2025
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the direction of blood flow through the heart. The opening and closing of the heart valves produce the heart-beat sounds.
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for:
- narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)
- leaking of the heart valve
Valve problems may be caused by infections (rheumatic fever) or birth defects and may cause heart failure (congestive heart failure) and infections (infective endocarditis).
The surgery is done while the patient is deep-asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia). An incision is made through the breast bone (sternum).
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood oxygenated and circulating while the heart is being operated on.
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human donors (cadavers), modified natural valves are from animal donors (porcine: pigs) which are placed in synthetic rings, and artificial valves are made of metal or plastic. Natural valves rarely require life-long medication to prevent blood clot formation (anticoagulation), whereas artificial valves will require anticoagulation.
The advantage of mechanical valves is that they last longer-thus, the tradeoff of lifelong anticoagulation in some cases is worth it to avoid a second valve replacement surgery.
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies depending on the heart valve and averages 2% to 5%. Approximately 2 out of 3 patients who received an artificial mitral valve are still alive 9 years after the surgery. Life-long anticoagulant therapy is necessary for patients with artificial heart valves. The clicking of the mechanical heart valve may be heard in the chest and is normal.
The first 2 or 3 days following the operation are spent in an intensive care unit where heart functions can be monitored constantly. The average hospital stay is 3 weeks. A few weeks to several months should be allowed for complete recovery, depending on health before surgery.






Animations
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Abdominal pain
- Aneurysm description
- Arrhythmias
- Atherosclerosis
- Atrial fibrillation
- Balloon angioplasty - short...
- Blood clotting
- Blood flow
- Blood pressure
- Brain components
- Cardiac and vascular disord...
- Cardiac arrhythmia - conduc...
- Cardiac arrhythmia symptoms
- Cardiac arrhythmia tests: E...
- Cardiac arrhythmia: Additio...
- Cardiac arrhythmia: Heart p...
- Cardiac arrhythmia: Physica...
- Cardiac arrhythmia: Taking ...
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac catheterization - a...
- Cardiac conduction system
- Cardiac CT scan overview
- Cardiomyopathy
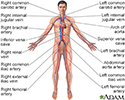
- Cardiovascular system
- Causes and side effects of ...
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Chest pain
- Childhood obesity
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Coronary artery bypass graf...
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary artery disease (CA...
- Electrocardiogram
- Epinephrine and exercise
- Erection problems
- Essential hypertension
- Exercise
- Hardening of arteries
- Healthy Guide to Fast Food
- Heart attack
- Heart bypass surgery
- Heart failure
- Heart formation
- Heartbeat
- How to use a pill cutter
- Hypertension
- Hypertension - overview
- Muscle types
- NICU consultants and suppor...
- Nuclear stress test
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Percutaneous transluminal c...
- Preeclampsia
- Smoking
- Smoking tips to quit
- Snoring
- Stent
- Stroke
- Stroke
- Stroke - secondary to cardi...
- Tachycardia
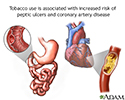
- Tobacco use - effects on ar...
- Tracking your blood pressur...
- Type 2 diabetes
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Vacation health care
- Valvular heart disease (VHD...
- Varicose veins
- Varicose veins overview
- Venous insufficiency
- What makes your heart beat?
Illustrations
- 15/15 rule
- Absent pulmonary valve
- Acute MI
- Adjustable gastric banding
- Aerobic exercise
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Angina
- Anomalous left coronary artery
- Anterior heart arteries
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic dissection
- Aortic rupture - chest x-ray
- Aortic stenosis
- Aortopulmonary window
- Arterial embolism
- Arterial plaque build-up
- Arterial tear in internal c...
- Arteries of the brain
- Artery cut section
- Atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis of internal...
- Atherosclerosis of the extr...
- Atrial septal defect
- Atrioventricular block - EC...
- Atrioventricular canal (end...
- Auscultation
- Bacterial pericarditis
- Balance receptors
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Biguanides
- Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD)
- Biliopancreatic diversion w...
- Biopsy catheter
- Blood pressure
- Blood pressure check
- Blood test
- Bradycardia
- Brain
- Brainstem function
- Breathing
- Bronchial cancer - CT scan
- Calcium benefit
- Calcium source
- Calories and fat per serving
- Cardiac arteriogram
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac catheterization
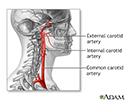
- Carotid dissection
- Carotid duplex
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Carotid stenosis - X-ray of...
- Cataract
- Cataract - close-up of the eye
- Central nervous system and ...
- Cerebellum - function
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Cholesterol
- Cholesterol producers
- Circle of Willis
- Circulation of blood throug...
- Circulatory system
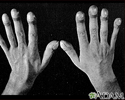
- Clubbing
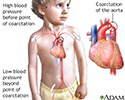
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Conduction system of the heart
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Coronary angiography
- Coronary artery blockage
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary artery fistula
- Coronary artery spasm
- Coronary artery stent
- Crossed eyes
- CT scan
- Culture-negative endocarditis
- Cyanosis of the nail bed
- Cyanotic heart disease
- DASH diet
- Deep veins
- Deep veins
- Deep venous thrombosis - il...
- Depressed nasal bridge
- Developmental process of at...
- Dextrocardia
- Diabetes and exercise
- Diabetic emergency supplies
- Digestive system
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Double aortic arch
- Double inlet left ventricle
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Drug induced hypertension
- Duplex/doppler ultrasound test
- Ear anatomy
- Ebstein's anomaly
- ECG
- ECMO
- Effects of age on blood pressure
- Eisenmenger syndrome (or co...
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Emphysema
- Endarterectomy
- Endocrine glands
- Enlarged view of atherosclerosis
- Exercise - a powerful tool
- Exercise 30 minutes a day
- Exercise can lower blood pr...
- Exercise with friends
- Eye
- Facial drooping
- Fast food
- Fish in diet
- Food and insulin release
- Food label guide for candy
- Food label guide for whole ...
- Foot swelling
- Fruits and vegetables
- Glucose in blood
- Glucose test
- Healthy diet
- Healthy diet
- Heart - front view
- Heart - section through the...
- Heart attack symptoms
- Heart beat
- Heart chambers
- Heart valves
- Heart valves - anterior view
- Heart valves - superior view
- High blood pressure tests
- Holter heart monitor
- Hypertension
- Hypertensive kidney
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Infective endocarditis
- Insulin pump
- Insulin pump
- Intracerebellar hemorrhage ...
- Intracerebral hemorrhage
- Janeway lesion on the finger
- Jaw pain and heart attacks
- Left atrial myxoma
- Left cerebral hemisphere - ...
- Left heart catheterization
- Leg pain (Osgood-Schlatter)
- Lifestyle changes
- Lobes of the brain
- Low blood sugar symptoms
- Lower leg edema
- Lower leg muscles
- Lung mass, right lung - CT scan
- Lung mass, right upper lobe...
- Lung nodule, right lower lu...
- Lung with squamous cell can...
- Lungs
- Lymph tissue in the head an...
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Mitral stenosis
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Monitoring blood pressure
- MRI scans
- MUGA test
- Muscular atrophy
- myPlate
- Neck pain
- Neck pulse
- Normal anatomy of the heart
- Normal heart anatomy (cut s...
- Normal heart rhythm
- Normal lung anatomy
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Otoscope examination
- Pacemaker
- Pericarditis
- Pericardium
- Pericardium
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Pharmacy options
- Pitting edema on the leg
- Plaque buildup in arteries
- Post myocardial infarction ...
- Posterior heart arteries
- Post-MI pericarditis
- Prevention of heart disease
- Progressive build-up of pla...
- Ptosis - drooping of the eyelid
- Pulmonary nodule, solitary ...
- Quitting smoking
- Radial pulse
- Read food labels
- Respiratory cilia
- Respiratory system
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis
- Right atrial myxoma
- Right cerebral hemisphere -...
- Roux-en-Y stomach surgery f...
- Saturated fats
- Secondhand smoke and lung cancer
- Shin splints
- Slit-lamp exam
- Smoking hazards
- Smoking hazards
- Sodium content
- Sources of fiber
- Stable angina
- Starchy foods
- Striae in the popliteal fossa
- Stroke
- Sulfonylureas drug
- Superficial thrombophlebitis
- Superficial thrombophlebitis
- Swan Ganz catheterization
- Taking your carotid pulse
- Thiazolidinediones
- Thoracic organs
- Thromboangiitis obliterans
- Thrombus
- Thyroid cancer - CT scan
- Tobacco and cancer
- Tobacco and chemicals
- Tobacco and vascular disease
- Tobacco health risks
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Totally anomalous pulmonary...
- Trans fatty acids
- Transient Ischemic attack (TIA)
- Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Type I diabetes
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, ventricular sep...
- Untreated hypertension
- Varicose veins
- Vascular ring
- Venous blood clot
- Ventricular septal defect
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
- Vertical banded gastroplasty
- Vertigo
- Visual acuity test
- Visual field test
- Vitamin B1 benefit
- Vitamin B1 source
- Vitamin C benefit
- Vitamin C deficit
- Vitamin C source
- Vitamin E and heart disease
- Warming up and cooling down
- Wine and health

 Bookmark
Bookmark