Multimedia Gallery






Heart valve surgery - series
Heart valve surgery - Series
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the direction of blood flow through the heart. The opening and closing of the heart valves produce the heart-beat sounds.
Heart valve surgery - series
Heart valve surgery - Series
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the directio...
Heart valve surgery - series
Indications
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for:
- narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)
- leaking of the heart valve
Valve problems may be caused by infections (rheumatic fever) or birth defects and may cause heart failure (congestive heart failure) and infections (infective endocarditis).
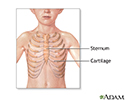
The surgery is done while the patient is deep-asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia). An incision is made through the breast bone (sternum).
Heart valve surgery - series
Indications
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for: narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)leaking of the heart valve Valve problems may be caused by inf...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 1
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood oxygenated and circulating while the heart is being operated on.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 1
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood ...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 2
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human donors (cadavers), modified natural valves are from animal donors (porcine: pigs) which are placed in synthetic rings, and artificial valves are made of metal or plastic. Natural valves rarely require life-long medication to prevent blood clot formation (anticoagulation), whereas artificial valves will require anticoagulation.
The advantage of mechanical valves is that they last longer-thus, the tradeoff of lifelong anticoagulation in some cases is worth it to avoid a second valve replacement surgery.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 2
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human ...
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 3
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
Heart valve surgery - series
Procedure, part 3
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
Heart valve surgery - series
Aftercare
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies depending on the heart valve and averages 2% to 5%. Approximately 2 out of 3 patients who received an artificial mitral valve are still alive 9 years after the surgery. Life-long anticoagulant therapy is necessary for patients with artificial heart valves. The clicking of the mechanical heart valve may be heard in the chest and is normal.
The first 2 or 3 days following the operation are spent in an intensive care unit where heart functions can be monitored constantly. The average hospital stay is 3 weeks. A few weeks to several months should be allowed for complete recovery, depending on health before surgery.
Heart valve surgery - series
Aftercare
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies dep...
Review Date: 1/27/2025
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
There are four valves in the heart: aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve. The valves are designed to control the direction of blood flow through the heart. The opening and closing of the heart valves produce the heart-beat sounds.
Heart valve replacement may be recommended for:
- narrowing of the heart valve (stenosis)
- leaking of the heart valve
Valve problems may be caused by infections (rheumatic fever) or birth defects and may cause heart failure (congestive heart failure) and infections (infective endocarditis).
The surgery is done while the patient is deep-asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia). An incision is made through the breast bone (sternum).
Heart valve surgery is open-heart surgery. Tubes are used to re-route the blood away from the heart to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood oxygenated and circulating while the heart is being operated on.
Valves may be repaired or replaced. Replacement heart valves are either natural (biologic) or artificial (mechanical). Natural valves are from human donors (cadavers), modified natural valves are from animal donors (porcine: pigs) which are placed in synthetic rings, and artificial valves are made of metal or plastic. Natural valves rarely require life-long medication to prevent blood clot formation (anticoagulation), whereas artificial valves will require anticoagulation.
The advantage of mechanical valves is that they last longer-thus, the tradeoff of lifelong anticoagulation in some cases is worth it to avoid a second valve replacement surgery.
The ineffective mitral valve is removed and the heart valve replacement is sutured into place.
The rate of success of heart valve surgery is high and increasing. The operation provides symptom relief and prolongs life. The death rate varies depending on the heart valve and averages 2% to 5%. Approximately 2 out of 3 patients who received an artificial mitral valve are still alive 9 years after the surgery. Life-long anticoagulant therapy is necessary for patients with artificial heart valves. The clicking of the mechanical heart valve may be heard in the chest and is normal.
The first 2 or 3 days following the operation are spent in an intensive care unit where heart functions can be monitored constantly. The average hospital stay is 3 weeks. A few weeks to several months should be allowed for complete recovery, depending on health before surgery.






Animations
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Abdominal pain
- ACL injury
- Acne
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Allergic rhinitis
- Allergies
- Allergy testing
- Allergy to mold - animal da...
- Alzheimer disease
- Alzheimer disease
- Anemia
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Anterior shoulder stretch
- Anti-reflux surgery
- Appendectomy
- Appendicitis
- Arm reach
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Atherosclerosis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Atrial fibrillation
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Bipolar disorder
- Bladder function - neurolog...
- Breast cancer
- Breast engorgement
- Breast lift
- Breast self-exam
- Breastfeeding
- Bronchitis
- Bronchoscopy
- Bunion
- Cardiac catheterization
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cataract
- Cataracts
- Cell division
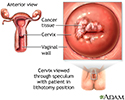
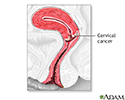
- Cervical cancer
- Cesarean section
- Chest pain
- Cholesterol and triglycerid...
- Chronic obstructive pulmona...
- Cluster headache
- Colon cancer
- Colorectal polyps
- Common cold
- Conception - general
- Conception - pregnancy
- Conception of identical twins
- Concussion
- Cosmetic surgery of the face
- Crohn disease
- C-section
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Dialysis
- Diarrhea
- Early labor
- Egg cell production
- Egg production
- Electrocardiogram
- Endometriosis
- Epilepsy
- Essential hypertension
- External rotation with band
- Fibromyalgia
- Flu
- Food poisoning
- Foot pain
- Formation of twins
- Gallstones
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Getting rid of lice in the home
- Glaucoma
- Hardening of arteries
- HbA1c
- Head injury
- Healthy Guide to Fast Food
- Hearing loss
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Heartburn
- Heel pain
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hernia
- Herniated disk
- Hip joint replacement
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- How to remove a splinter
- How to treat a nosebleed
- How to treat a sunburn
- How to use a peak flow meter
- How to use a pill cutter
- How to use eye drops
- How to use nasal sprays
- Hypertension
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Hysterectomy
- Insomnia
- Internal rotation with band
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Isometric
- Kidney stones
- Kidney stones
- Knee joint replacement
- Let's talk about pink eye
- Liposuction
- Lung cancer
- Lyme disease
- Lymphatics and the breast
- Melanoma
- Menopause
- Migraine
- Multiple sclerosis
- Nasal congestion
- Neck pain
- Nuclear stress test
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis
- Ovulation
- Pap smear
- Pendulum exercise
- Peptic ulcer
- Pharyngitis
- Placenta delivery
- Placenta formation
- Plantar fasciitis
- Pneumonia
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy care
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff problems
- Rupturing membranes
- Sciatica
- Seizures
- Shingles
- Shoulder blade retraction
- Shoulder blade retraction w...
- Shoulder pain
- Sinusitis
- Sleep disorders
- Smoking tips to quit
- Snoring
- Spinal stenosis
- Stent
- Storing breast milk
- Strep throat
- Stretching back of your shoulder
- Stroke
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Tension headache
- The difference between a co...
- The role of amniotic fluid
- Tips on buying cold and flu...
- Tips on removing ear wax
- Tracking your blood pressur...
- Treating eyelid bumps
- Twin-to-twin transfusion sy...
- Type 2 diabetes
- Ulcerative colitis
- Ultrasound
- Understanding cholesterol r...
- Up the back stretch
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary tract infection - adults
- Uterine fibroids
- Vacation health care
- Vaginal delivery
- Varicose veins
- Venous insufficiency
- Wall push-up
- Wall stretch
- Warts
- What are hives?
- What causes wheezing?
- What in the world is a neti pot?
- What is tennis elbow?
- What makes your heart beat?
- What to do when something g...
Illustrations
- 3D ultrasound
- Abnormal discharge from the...
- Abnormal menstrual periods
- Absence of menstruation (am...
- Amniocentesis
- Amniotic fluid
- Anatomy of a normal placenta
- Anterior vaginal wall repair
- Bleeding between periods
- Breast infection
- Breast lumps
- Breast pain
- Breast self-exam
- Breast self-exam
- Breast self-exam
- Breastfeeding
- Causes of breast lumps
- Causes of breast lumps
- Causes of painful intercourse
- Causes of sexual dysfunction
- Causes of vaginal itching
- Cervical biopsy
- Cervical cancer
- Cervical cancer
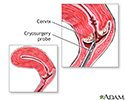
- Cervical cryosurgery
- Cervical cryosurgery
- Cervical erosion
- Cervical neoplasia
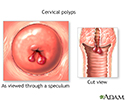
- Cervical polyps
- Cervicitis
- Cervix needle sample
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Childbirth
- Cold cone removal
- Colposcopy-directed biopsy
- Culdocentesis
- D and C
- Delivery presentations
- Depression and the menstrua...
- Developmental disorders of ...
- Early pregnancy
- Early weeks of pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Emergency Childbirth
- Emergency Childbirth
- Endometrial biopsy
- Endometrial biopsy
- Endometrial cancer
- Endometriosis
- Endometritis
- Episiotomy aftercare
- Excision of breast lump
- Female breast
- Female perineal anatomy
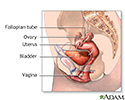
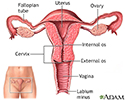
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy...
- Female urinary tract
- Female-pattern baldness
- Fibrocystic breast change
- Fibroid tumors
- First trimester of pregnancy
- Folic acid
- Genetic counseling and pren...
- Gestational ages
- Gestational diabetes
- Hysterectomy
- Inflatable artificial sphincter
- Intraductal papilloma
- Lumpectomy
- Mammary gland
- Mammography
- Mammoplasty
- Menopause
- Morning sickness
- Nabothian cyst
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabe...
- Needle biopsy of the breast
- Normal female anatomy
- Normal female breast anatomy
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Open biopsy of the breast
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Ovarian cancer
- Ovarian cancer dangers
- Ovarian cancer metastasis
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian cysts
- Ovarian growth worries
- Pap smear
- Pap smear
- Pap smears and cervical cancer
- Pelvic adhesions
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Peritoneal and ovarian canc...
- Placenta
- Placenta
- Placenta
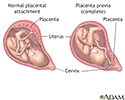
- Placenta previa
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy test
- Premenstrual bloating
- Prevention of cystitis
- Primary amenorrhea
- Relief of menstrual cramps
- Relieving PMS
- Rotator cuff muscles
- Secondary amenorrhea
- Side sectional view of fema...
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Stress incontinence
- Stress incontinence
- Teratoma - MRI scan
- The wet mount vaginitis test
- Threatened miscarriage
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Ultrasound comparison
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
- Ureteral biopsy
- Uterine anatomy
- Uterus
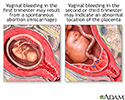
- Vaginal bleeding during pre...
- Vaginal discharge
- Yeast infections
Presentations
- Achalasia - series
- Adenoid removal - series
- Animal bite - first aid - series
- Ankle sprain - Series
- Appendectomy - series
- Bone fracture repair - series
- Bone-marrow transplant - series
- Bruise healing - series
- Cataract surgery - series
- Chest tube insertion - series
- Choking first aid - adult o...
- Choking first aid - infant ...
- Circumcision - series
- Cleft lip repair - series
- Clubfoot repair - series
- Colon cancer - series
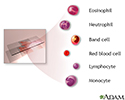
- Complete blood count - series
- Convulsions - first aid - series
- CPR - child 1 to 8 years ol...
- CPR - infant - series
- Craniotomy - series
- Diaphragmatic hernia repair...
- Ear tube insertion - series
- Eardrum repair - series
- Emergency airway puncture ...
- Exchange transfusion - series
- Gastroesophageal reflux - series
- Gastroschisis repair - series
- Heart valve surgery - series
- Hemangioma excision - series
- Hiatal hernia repair - series
- Hydrocele repair - series
- Hypospadias repair - series
- Imperforate anus repair - ...
- Infantile pyloric stenosis ...
- Inflammatory bowel disease ...
- Inguinal hernia repair - series
- Intestinal obstruction (ped...
- Intestinal obstruction repa...
- Large bowel resection - series
- Leg lengthening - series
- Mastoidectomy - series
- Meckel's diverticulectomy ...
- Meningocele repair - series
- Metered dose inhaler use - ...
- Minor burn - first aid - series
- Minor cut - first aid
- Monitoring blood glucose - ...
- Nebulizer use - series
- Omphalocele repair - series
- Pancreatitis - series
- Patent ductus arteriosis (P...
- Patent urachus repair - series
- Pectus excavatum repair - ...
- Pneumothorax - series
- Repair of webbed fingers -...
- Retinal detachment repair ...
- Rh incompatibility - series
- Small bowel resection - series
- Spleen removal - series
- Thyroidectomy - series
- Tonsillectomy - series
- Tracheoesophageal fistula r...
- Two person roll - series
- Umbilical hernia repair - ...
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt ...
- White blood cell count - series

 Bookmark
Bookmark